APETx4, a Novel Sea Anemone Toxin and a Modulator of the Cancer-Relevant Potassium Channel KV10.1
- PMID: 28902151
- PMCID: PMC5618426
- DOI: 10.3390/md15090287
APETx4, a Novel Sea Anemone Toxin and a Modulator of the Cancer-Relevant Potassium Channel KV10.1
Abstract
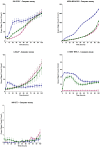
The human ether-à-go-go channel (hEag1 or KV10.1) is a cancer-relevant voltage-gated potassium channel that is overexpressed in a majority of human tumors. Peptides that are able to selectively inhibit this channel can be lead compounds in the search for new anticancer drugs. Here, we report the activity-guided purification and electrophysiological characterization of a novel KV10.1 inhibitor from the sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima. Purified sea anemone fractions were screened for inhibitory activity on KV10.1 by measuring whole-cell currents as expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes using the two-microelectrode voltage clamp technique. Fractions that showed activity on Kv10.1 were further purified by RP-HPLC. The amino acid sequence of the peptide was determined by a combination of MALDI- LIFT-TOF/TOF MS/MS and CID-ESI-FT-ICR MS/MS and showed a high similarity with APETx1 and APETx3 and was therefore named APETx4. Subsequently, the peptide was electrophysiologically characterized on KV10.1. The selectivity of the toxin was investigated on an array of voltage-gated ion channels, including the cardiac human ether-à-go-go-related gene potassium channel (hERG or Kv11.1). The toxin inhibits KV10.1 with an IC50 value of 1.1 μM. In the presence of a similar toxin concentration, a shift of the activation curve towards more positive potentials was observed. Similar to the effect of the gating modifier toxin APETx1 on hERG, the inhibition of Kv10.1 by the isolated toxin is reduced at more positive voltages and the peptide seems to keep the channel in a closed state. Although the peptide also induces inhibitory effects on other KV and NaV channels, it exhibits no significant effect on hERG. Moreover, APETx4 induces a concentration-dependent cytotoxic and proapoptotic effect in various cancerous and noncancerous cell lines. This newly identified KV10.1 inhibitor can be used as a tool to further characterize the oncogenic channel KV10.1 or as a scaffold for the design and synthesis of more potent and safer anticancer drugs.
Keywords: APETx; KV10.1; cancer; potassium channel; sea anemone peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
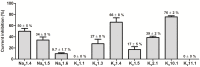


References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Cancer: Fact Sheet. February 2017. [(accessed on 14 June 2017)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/
-
- American Cancer Society Global Cancer Facts & Figures 3rd Edition. Am. Cancer Soc. 2015 doi: 10.1002/ijc.27711. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

