Whispering-Gallery Mode Resonators for Detecting Cancer
- PMID: 28902169
- PMCID: PMC5621035
- DOI: 10.3390/s17092095
Whispering-Gallery Mode Resonators for Detecting Cancer
Abstract
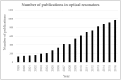
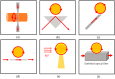
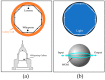
Optical resonators are sensors well known for their high sensitivity and fast response time. These sensors have a wide range of applications, including in the biomedical fields, and cancer detection is one such promising application. Sensor diagnosis currently has many limitations, such as being expensive, highly invasive, and time-consuming. New developments are welcomed to overcome these limitations. Optical resonators have high sensitivity, which enable medical testing to detect disease in the early stage. Herein, we describe the principle of whispering-gallery mode and ring optical resonators. We also add to the knowledge of cancer biomarker diagnosis, where we discuss the application of optical resonators for specific biomarkers. Lastly, we discuss advancements in optical resonators for detecting cancer in terms of their ability to detect small amounts of cancer biomarkers.
Keywords: biosensor; cancer; evanescent wave; instrumentation; label-free; optical resonator; optical waveguide; sensor platform; whispering-gallery mode.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
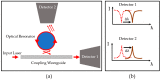
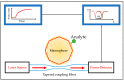
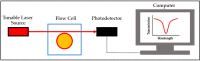
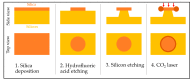



Similar articles
-
Label-Free Biological and Chemical Sensing Using Whispering Gallery Mode Optical Resonators: Past, Present, and Future.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Mar 8;17(3):540. doi: 10.3390/s17030540. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28282881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptasensors Based on Whispering Gallery Mode Resonators.Biosensors (Basel). 2016 Jul 16;6(3):28. doi: 10.3390/bios6030028. Biosensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27438861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Whispering Gallery Mode Resonators to Biochemical Sensors.ACS Sens. 2023 Jul 28;8(7):2440-2470. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.2c02876. Epub 2023 Jun 30. ACS Sens. 2023. PMID: 37390481 Review.
-
Label-Free Optical Resonator-Based Biosensors.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 19;20(20):5901. doi: 10.3390/s20205901. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33086566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whispering-gallery mode-based optical biosensing: A review on development and applications in ultrasensitive biological detection and bioimaging.Anal Chim Acta. 2025 Aug 22;1364:344249. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2025.344249. Epub 2025 May 28. Anal Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 40480684 Review.
Cited by
-
Whispering Gallery Mode Resonators for Precision Temperature Metrology Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Apr 17;21(8):2844. doi: 10.3390/s21082844. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920723 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Tungsten Disulphide Coating on Tapered Microfiber for Relative Humidity Sensing Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 27;21(21):7132. doi: 10.3390/s21217132. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34770442 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on Assembling Coronavirus Spikes on Fiber Optics to Reveal Broadly Recognizing Antibodies and Generate a Universal Coronavirus Detector.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Nov 26;9:637715. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.637715. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34900951 Free PMC article.
-
In-Fiber BaTiO3 Microsphere Resonator for High-Sensitivity Temperature Measurement.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;12(3):318. doi: 10.3390/mi12030318. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803684 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Dielectric Waveguide Grating and Fabry-Perot Modes in Elastic Grating in Optical Detection of Ultrasound.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jun 14;21(12):4081. doi: 10.3390/s21124081. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34198475 Free PMC article.
References
-
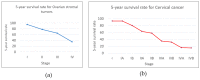
- Cancer Research UK Worldwide Cancer Statistics. [(accessed on 28 June 2017)]; Available online: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/wo....
-
- American Cancer Society Survival Rates for Hodgkin Lymphoma By Stage. [(accessed on 28 June 2017)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/hodgkin-lymphoma/detection-diagnosis-stagi....
-
- American Cancer Society How Are Lung Carcinoid Tumors Staged? [(accessed on 28 June 2017)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-carcinoid-tumor/detection-diagnosis-s....
-
- Cancer Research UK Stages of Cancer. [(accessed on 28 June 2017)]; Available online: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/what-is-cancer/stages-of-ca....
-
- American Cancer Society Survival Rates for Ovarian Cancer, by Stage. [(accessed on 28 June 2017)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/ovarian-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

