Biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids part I
- PMID: 28902434
- PMCID: PMC6421866
- DOI: 10.1002/med.21466
Biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids part I
Abstract
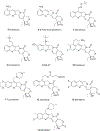
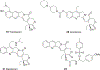
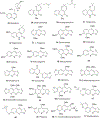
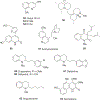
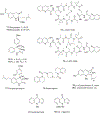
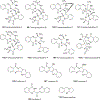
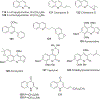
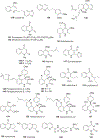
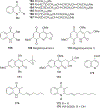
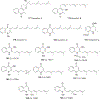
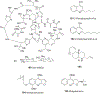
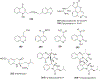
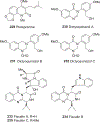
Quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids, two important classes of N-based heterocyclic compounds, have attracted tremendous attention from researchers worldwide since the 19th century. Over the past 200 years, many compounds from these two classes were isolated from natural sources, and most of them and their modified analogs possess significant bioactivities. Quinine and camptothecin are two of the most famous and important quinoline alkaloids, and their discoveries opened new areas in antimalarial and anticancer drug development, respectively. In this review, we survey the literature on bioactive alkaloids from these two classes and highlight research achievements prior to the year 2008 (Part I). Over 200 molecules with a broad range of bioactivities, including antitumor, antimalarial, antibacterial and antifungal, antiparasitic and insecticidal, antiviral, antiplatelet, anti-inflammatory, herbicidal, antioxidant and other activities, were reviewed. This survey should provide new clues or possibilities for the discovery of new and better drugs from the original naturally occurring quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids.
Keywords: bioactivities; camptothecin; quinazoline alkaloids; quinine; quinoline alkaloids.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
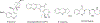


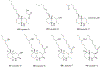



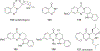


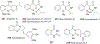

References
-
- Prajapati SM, Patel KD, Vekariya RH, Panchal SN, Patel HD. Recent advances in the synthesis of quinolines: a review. RSC Adv. 2014;4:24463–24476.
-
- Wiesner J, Ortmann R, Jomaa H, Schlitzer M. New antimalarial drugs. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2003;42:5274–5293. - PubMed
-
- Manske RH. The chemistry of quinolines. Chem Rev. 1942;30:113–144.
-
- Tumer RR, Woodward RR. The chemistry of the Cinchona alkaloids. In: Manske RHF, ed. The Alkaloids. New York: Academic Press; 1953:16.
-
- Wall ME, Wani MC, Cook CE, Palmer KH, McPhail AT, Sim GA. Plant antitumor agents. I. The isolation and structure of camptothecin, a novel alkaloidal leukemia and tumor inhibitor from Camptotheca acuminate. J Am Chem Soc. 1966;88:3888–3890.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

