The neuropeptide NMU amplifies ILC2-driven allergic lung inflammation
- PMID: 28902842
- PMCID: PMC5746044
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24029
The neuropeptide NMU amplifies ILC2-driven allergic lung inflammation
Erratum in
-
Erratum: The neuropeptide NMU amplifies ILC2-driven allergic lung inflammation.Nature. 2017 Nov 30;551(7682):658. doi: 10.1038/nature24480. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29143821
Abstract
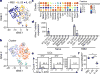
Type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) both contribute to mucosal homeostasis and initiate pathologic inflammation in allergic asthma. However, the signals that direct ILC2s to promote homeostasis versus inflammation are unclear. To identify such molecular cues, we profiled mouse lung-resident ILCs using single-cell RNA sequencing at steady state and after in vivo stimulation with the alarmin cytokines IL-25 and IL-33. ILC2s were transcriptionally heterogeneous after activation, with subpopulations distinguished by expression of proliferative, homeostatic and effector genes. The neuropeptide receptor Nmur1 was preferentially expressed by ILC2s at steady state and after IL-25 stimulation. Neuromedin U (NMU), the ligand of NMUR1, activated ILC2s in vitro, and in vivo co-administration of NMU with IL-25 strongly amplified allergic inflammation. Loss of NMU-NMUR1 signalling reduced ILC2 frequency and effector function, and altered transcriptional programs following allergen challenge in vivo. Thus, NMUR1 signalling promotes inflammatory ILC2 responses, highlighting the importance of neuro-immune crosstalk in allergic inflammation at mucosal surfaces.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures










Comment in
-
Neuroimmunology: ILC2s touch a nerve.Nat Rev Immunol. 2017 Nov;17(11):661. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.119. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29034906 No abstract available.
-
Can U Turn ILC2s Up?Cell. 2017 Nov 2;171(4):742-744. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.013. Cell. 2017. PMID: 29100072
-
Immunology: The Neuronal Pathway to Mucosal Immunity.Curr Biol. 2018 Jan 8;28(1):R33-R36. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.11.025. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29316420
References
-
- Gudbjartsson DF, et al. Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat Genet. 2009;41:342–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 HL130540/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA180922/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130019/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI039671/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R50 CA211461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI095608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI061570/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI097333/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004085/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 AT009499/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI074878/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 OD003930/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095466/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL122531/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI102942/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004080/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI087990/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI123516/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI083480/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

