Correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter with directly measured intracranial pressure in Korean adults using bedside ultrasonography
- PMID: 28902893
- PMCID: PMC5597178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183170
Correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter with directly measured intracranial pressure in Korean adults using bedside ultrasonography
Abstract
Objectives: The correlation of optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) as seen on ultrasonography (US) and directly measured intracranial pressure (ICP) has been well described. Nevertheless, differences in ethnicity and type of ICP monitor used are obstacles to the interpretation. Therefore, we investigated the direct correlation between ONSD and ventricular ICP and defined an optimal cut-off point for identifying increased ICP (IICP) in Korean adults with brain lesions.
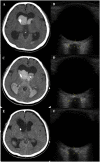
Methods: This prospective study included patients who required an external ventricular drainage (EVD) catheter for ICP control. IICP was defined as an opening pressure over 20 mmHg. ONSD was measured using a 13 MHz US probe before the procedure. Linear regression analysis and receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve were used to assess the association between ONSD and ICP. Optimal cut-off value for identifying IICP was defined.
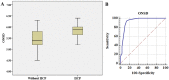
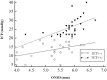
Results: A total of 62 patients who underwent ONSD measurement with simultaneous EVD catheter placement were enrolled in this study. Thirty-two patients (51.6%) were found to have IICP. ONSD in patients with IICP (5.80 ± 0.45 mm) was significantly higher than in those without IICP (5.30 ± 0.61 mm) (P < 0.01). The IICP group showed more significant linear correlation with ONSD (r = 0.57, P < 0.01) compared to the non-IICP group (r = 0.42, P = 0.02). ONSD > 5.6 mm disclosed a sensitivity of 93.75% and a specificity of 86.67% for identifying IICP.
Conclusion: ONSD as seen on bedside US correlated well with directly measured ICP in Korean adults with brain lesions. The optimal cut-off point of ONSD for detecting IICP was 5.6 mm.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Li ZM Q Zhe MD; Zhang Ning MD; Zhao Jun MD; Shen Dongqing MD. Comparison Between Intraventricular and Intraparenchymal Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Asian Patients With Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurosurgery Quarterly. 2016;26(2):5.
-
- Blaivas M, Theodoro D, Sierzenski PR. Elevated intracranial pressure detected by bedside emergency ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath. Acad Emerg Med. 2003;10(4):376–81. . - PubMed
-
- Girisgin AS, Kalkan E, Kocak S, Cander B, Gul M, Semiz M. The role of optic nerve ultrasonography in the diagnosis of elevated intracranial pressure. Emerg Med J. 2007;24(4):251–4. doi: 10.1136/emj.2006.040931 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tayal VS, Neulander M, Norton HJ, Foster T, Saunders T, Blaivas M. Emergency department sonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter to detect findings of increased intracranial pressure in adult head injury patients. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;49(4):508–14. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.06.040 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

