Self-Assembled 2D Free-Standing Janus Nanosheets with Single-Layer Thickness
- PMID: 28902999
- PMCID: PMC5632812
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b06591
Self-Assembled 2D Free-Standing Janus Nanosheets with Single-Layer Thickness
Abstract
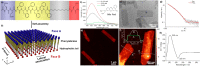
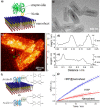
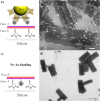
We report the thermodynamically controlled growth of solution-processable and free-standing nanosheets via peptide assembly in two dimensions. By taking advantage of self-sorting between peptide β-strands and hydrocarbon chains, we have demonstrated the formation of Janus 2D structures with single-layer thickness, which enable a predetermined surface heterofunctionalization. A controlled 2D-to-1D morphological transition was achieved by subtly adjusting the intermolecular forces. These nanosheets provide an ideal substrate for the engineering of guest components (e.g., proteins and nanoparticles), where enhanced enzyme activity was observed. We anticipate that sequence-specific programmed peptides will offer promise as design elements for 2D assemblies with face-selective functionalization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

