Genetic variation and forensic characteristic analysis of 25 STRs of a novel fluorescence co-amplification system in Chinese Southern Shaanxi Han population
- PMID: 28903432
- PMCID: PMC5589671
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19317
Genetic variation and forensic characteristic analysis of 25 STRs of a novel fluorescence co-amplification system in Chinese Southern Shaanxi Han population
Abstract
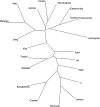
We analyzed the genetic polymorphisms of 15 autosomal and 10 Y-chromosomal STR loci in 214 individuals of Han population from Southern Shaanxi of China and studied the genetic relationships between Southern Shaanxi Han and other populations. We observed a total of 150 alleles at 15 autosomal STR loci with the corresponding allelic frequencies ranging from 0.0023 to 0.5210, and the combined power of discrimination and exclusion for the 15 autosomal STR loci were 0.99999999999999998866 and 0.999998491, respectively. For the 10 Y-STR loci, totally 100 different haplotypes were obtained, of which 94 were unique. The discriminatory capacity and haplotype diversity values of the 10 Y-STR loci were 0.9259 and 0.998269, respectively. The results demonstrated high genetic diversities of the 25 STR loci in the population for forensic applications. We constructed neighbor-joining tree and conducted principal component analysis based on 15 autosomal STR loci and conducted multidimensional scaling analysis and constructed neighbor-joining tree based on 10 Y-STR loci. The results of population genetic analyses based on both autosomal and Y-chromosome STRs indicated that the studied Southern Shaanxi Han population had relatively closer genetic relationship with Eastern Han population, and distant relationships with Croatian, Serbian and Moroccan populations.
Keywords: Southern Shaanxi Han population; Y-STR; autosomal STR; forensic characteristic analysis; genetic polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Allelic and haplotypic polymorphisms and paternal genetic analysis of Chinese Shaanxi Han population utilizing a multiplex Y-STR set.Ann Hum Biol. 2022 Dec;49(7-8):361-366. doi: 10.1080/03014460.2022.2152487. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Ann Hum Biol. 2022. PMID: 36437608
-
Genetic polymorphisms, forensic efficiency and phylogenetic analysis of 17 autosomal STR loci in the Han population of Wuxi, Eastern China.Ann Hum Biol. 2019 Dec;46(7-8):601-605. doi: 10.1080/03014460.2019.1693628. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Ann Hum Biol. 2019. PMID: 31790285
-
Population genetic analysis of Shaanxi male Han Chinese population reveals genetic differentiation and homogenization of East Asians.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 May;8(5):e1209. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1209. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. Retraction in: Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2024 Feb;12(2):e2375. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2375. PMID: 32163678 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Genetic characterisation for Yan'an Han population in Northern Shaanxi Province, China, via 38Y-STRs using Yfiler™ Platinum.Ann Hum Biol. 2021 Jun;48(4):327-334. doi: 10.1080/03014460.2021.1951350. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Ann Hum Biol. 2021. PMID: 34308740
-
Haplotype diversity and phylogenetic relationship analysis of Chinese Yulin Han population using 59 Y-STR loci of two novel Y-STR typing systems.Leg Med (Tokyo). 2021 May;50:101871. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2021.101871. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 33756375
Cited by
-
Forensic characteristics and phylogenetic analyses of one branch of Tai-Kadai language-speaking Hainan Hlai (Ha Hlai) via 23 autosomal STRs included in the Huaxia™ Platinum System.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Oct;8(10):e1462. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1462. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. Retraction in: Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2024 Feb;12(2):e2379. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2379. PMID: 32862500 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Zhu BF, Zhang YD, Shen CM, Du WA, Liu WJ, Meng HT, Wang HD, Yang G, Jin R, Yang CH, Yan JW, Bie XH. Developmental validation of the AGCU 21+1 STR kit: a novel multiplex assay for forensic application. Electrophoresis. 2015;36:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Meng HT, Zhang LP, Wu H, Yang CH, Chen JG, Wang Y, Yan JW, Wang HD, Zhang YD, Liu WJ, Zhu BF. Genetic diversities of 20 novel autosomal STRs in Chinese Xibe ethnic group and its genetic relationships with neighboring populations. Gene. 2015;557:222–228. - PubMed
-
- Zhang S, Tian H, Wang Z, Zhao S, Hu Z, Li C, Ji C. Development of a new 26plex Y-STRs typing system for forensic application. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014;13:112–120. - PubMed
-
- Jobling MA, Tyler-Smith C. The human Y chromosome: an evolutionary marker comes of age. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:598–612. - PubMed
-
- Jobling MA, Tyler-Smith C. Fathers and sons: the Y chromosome and human evolution. Trends Genet. 1995;11:449–456. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

