Combination of Tumor Volume and Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Improved Prognostic Stratification of Stage II Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in the Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy Era: A Large-Scale Cohort Study
- PMID: 28903550
- PMCID: PMC6056955
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2017.237
Combination of Tumor Volume and Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Improved Prognostic Stratification of Stage II Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in the Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy Era: A Large-Scale Cohort Study
Abstract
Purpose: Little is known about combination of the circulating Epstein-Barr viral (EBV) DNA and tumor volume in prognosis of stage II nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients in the intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) era. We conducted this cohort study to evaluate the prognostic values of combining these two factors.
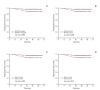
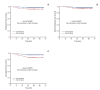
Materials and methods: By Kaplan-Meier, we compare the differences of survival curves between 385 patients with different EBV DNA or tumor volume levels, or with the combination of two biomarkers mentioned above.
Results: Gross tumor volume of cervical lymph nodes (GTVnd, p < 0.001) and total tumor volume (GTVtotal, p < 0.001) were both closely related to pretreatment EBV DNA, while gross tumor volume of nasopharynx (GTVnx, p=0.047) was weakly related to EBV DNA. EBV DNA was significantly correlated with progress-free survival (PFS, p=0.005), locoregional-free survival (LRFS, p=0.039), and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS, p=0.017), while GTVtotal, regardless of GTVnx and GTVnd, had a significant correlation with PFS and LRFS. The p-values of GTVtotal for PFS and LRFS were 0.008 and 0.001, respectively. According to GTVtotal and pretreatment EBV DNA level, patients were divided into a low-risk group (EBV DNA 0 copy/mL, GTVtotal < 30 cm3; EBV DNA 0 copy/mL, GTVtotal ≥ 30 cm3; or EBV DNA > 0 copy/mL, GTVtotal < 30 cm3) and a high-risk group (EBV DNA > 0 copy/mL, GTVtotal ≥ 30 cm3). When patients in the low-risk group were compared with those in the high-risk group, 3-year PFS (p=0.003), LRFS (p=0.010), and DMFS (p=0.031) rates were statistically significant.
Conclusion: Pretreatment plasma EBV DNA and tumor volume were both closely correlated with prognosis of stage II NPC patients in the IMRT era. Combination of EBV DNA and tumor volume can refine prognosis and indicate for clinical therapy.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; Intensity modulated radiotherapy; Prognosis; Tumor burden; Nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures

References
-
- Choa G. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Some observations on the clinical features and technique of examination. Pac Med Surg. 1967;75:172–4. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Ng WT, Chan YH, Sze H, Chan C, Lam TH. The battle against nasopharyngeal cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2012;104:272–8. - PubMed
-
- Wee JT, Ha TC, Loong SL, Qian CN. Is nasopharyngeal cancer really a "Cantonese cancer"? Chin J Cancer. 2010;29:517–26. - PubMed
-
- Chen QY, Wen YF, Guo L, Liu H, Huang PY, Mo HY, et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy vs radiotherapy alone in stage II nasopharyngeal carcinoma: phase III randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:1761–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

