Identification and characterization of the novel reversible and selective cathepsin X inhibitors
- PMID: 28904354
- PMCID: PMC5597618
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11935-1
Identification and characterization of the novel reversible and selective cathepsin X inhibitors
Abstract
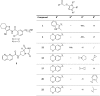
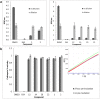
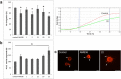
Cathepsin X is a cysteine peptidase involved in the progression of cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Targeting this enzyme with selective inhibitors opens a new possibility for intervention in several therapeutic areas. In this study triazole-based reversible and selective inhibitors of cathepsin X have been identified. Their selectivity and binding is enhanced when the 2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]dioxine moiety is present as the R1 substituent. Of a series of selected triazole-benzodioxine derivatives, compound 22 is the most potent inhibitor of cathepsin X carboxypeptidase activity (Ki = 2.45 ± 0.05 μM) with at least 100-fold greater selectivity in comparison to cathepsin B or other related cysteine peptidases. Compound 22 is not cytotoxic to prostate cancer cells PC-3 or pheochromocytoma PC-12 cells at concentrations up to 10 μM. It significantly inhibits the migration of tumor cells and increases the outgrowth of neurites, both processes being under the control of cathepsin X carboxypeptidase activity. Compound 22 and other characterized triazole-based inhibitors thus possess a great potential for further development resulting in several in vivo applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure-activity relationships of triazole-benzodioxine inhibitors of cathepsin X.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 May 1;193:112218. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112218. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32208223
-
Dioxo-triazines as a novel series of cathepsin K inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 Mar 1;20(5):1488-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.01.116. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010. PMID: 20153187
-
Advances in the discovery of cathepsin K inhibitors on bone resorption.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2018 Dec;33(1):890-904. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1465417. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29723068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly selective azadipeptide nitrile inhibitors for cathepsin K: design, synthesis and activity assays.Org Biomol Chem. 2013 Feb 21;11(7):1143-8. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26624e. Org Biomol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23299878
-
Peptidomimetic inhibitors of cathepsin K.Curr Top Med Chem. 2010;10(7):745-51. doi: 10.2174/156802610791113450. Curr Top Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20337585 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of Cathepsin X in Glioblastoma: Interplay with γ-Enolase and the Effects of Selective Cathepsin X Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):1784. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031784. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163706 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin X Activity Does Not Affect NK-Target Cell Synapse but Is Rather Distributed to Cytotoxic Granules.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 16;22(24):13495. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413495. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948293 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of enolase activation to promote neural protection and regeneration in spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Jul;18(7):1457-1462. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.361539. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36571342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteine cathepsins L and X differentially modulate interactions between myeloid-derived suppressor cells and tumor cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020 Sep;69(9):1869-1880. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02592-x. Epub 2020 May 5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32372139 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of novel cathepsin-X inhibitors in vitro and in vivo and their ability to improve cathepsin-B-directed antitumor therapy.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jan 6;79(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04117-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 34989869 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

