Biophysical technologies for understanding circulating tumor cell biology and metastasis
- PMID: 28904890
- PMCID: PMC5583073
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr.2017.05.08
Biophysical technologies for understanding circulating tumor cell biology and metastasis
Abstract
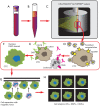
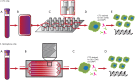
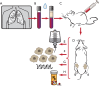
An understanding of cancer evolution in lung cancer with its associated resistance to therapy can only be achieved with repeated sampling and analysis of the cancer. Given the high risks and costs associated with repeat physical biopsy, alternative technologies must be applied. Several modalities exist for analysis and re-analysis of cancer biology. Among them are the CellSearch platform, the CTC chip, and the high-definition CTC platform. While the former is primarily able to provide prognosticating information in the form of CTC enumeration, the latter two have the advantage of serving as a platform to study tumor biology. Techniques for analysis of single cell genomics, as well as protein expression on a single cell basis provide scientists with the capacity to understand cancer cell populations as a collection of individual cells, rather than as an average of all cells. A multimodal combination of circulating tumor DNAs (ctDNAs), CTCs, proteomics, and CTC-derived xenografts (CDXs) to create computational models useful in diagnosis, prognostication, and predictiveness to treatment is likely the future of tailoring individualized cancer care.
Keywords: CellSearch; Circulating tumor cells (CTCs); lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of circulating tumor cells using a novel workflow combining the CellSearch® system and the CellCelector™.Biotechnol Prog. 2017 Jan;33(1):125-132. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2294. Epub 2016 May 17. Biotechnol Prog. 2017. PMID: 27126369
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition leads to disease-stage differences in circulating tumor cell detection and metastasis in pre-clinical models of prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):76125-76139. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12682. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27764810 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective assessment of the prognostic value of circulating tumor cells and their clusters in patients with advanced-stage breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Dec;154(3):563-71. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3636-4. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26573830
-
Prospects for Comprehensive Analyses of Circulating Tumor Cells in Tumor Biology.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 1;12(5):1135. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051135. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32369927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond Enumeration: Functional and Computational Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells to Investigate Cancer Metastasis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Feb 19;5:34. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00034. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29520361 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A pilot study of cdc6 as a biomarker for circulating tumor cells in patients with lung cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jun;34(6):e23245. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23245. Epub 2020 Apr 6. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32249466 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Circulating Tumor DNA into Clinical Management of Colorectal Cancer: Practical Implications and Therapeutic Challenges.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 30;17(15):2520. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152520. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Tumor Cells: From the Laboratory to the Cancer Clinic.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 21;12(9):2361. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092361. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32825548 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Utility of Liquid Biopsy as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Tool for the Assessment of Solid Tumors: Implications in the Precision Oncology.J Clin Med. 2019 Mar 18;8(3):373. doi: 10.3390/jcm8030373. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 30889786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liquid Biopsy in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: State of the Art, Pitfalls, and Perspectives.Front Oncol. 2019 Aug 14;9:740. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00740. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31475103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
