The Effect of Oral Dexmedetomidine Premedication on Preoperative Cooperation and Emergence Delirium in Children Undergoing Dental Procedures
- PMID: 28904966
- PMCID: PMC5585600
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/6742183
The Effect of Oral Dexmedetomidine Premedication on Preoperative Cooperation and Emergence Delirium in Children Undergoing Dental Procedures
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this study was to detect the effect of 1 μg/kg of oral dexmedetomidine (DEX) as premedication among children undergoing dental procedures.
Materials and methods: The study involved 100 children between 2 and 6 years of age, ASA I, who underwent full-mouth dental rehabilitation. The DEX group (n = 50) received 1 μg/kg DEX in apple juice, and the control group (n = 50) received only apple juice. The patients' scores on the Ramsay Sedation Scale (RSS), parental separation anxiety scale, mask acceptance scale, and pediatric anesthesia emergence delirium scale (PAEDS) and hemodynamic parameters were recorded. The data were analyzed using chi-square test, Fisher's exact test, Student's t-test, and analysis of variance in SPSS.
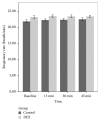
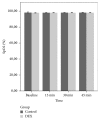
Results: RSS scores were significantly higher in the DEX group than group C at 15, 30, and 45 min (p < 0.05). More children (68% easy separation, 74% satisfactory mask acceptance) in the DEX group showed satisfactory ease of parental separation and mask acceptance behavior (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the PAEDS scores and mean hemodynamic parameters of both groups.
Conclusions: Oral DEX administered at 1 μg/kg provided satisfactory sedation levels, ease of parental separation, and mask acceptance in children but was not effective in preventing emergence delirium. The trial was registered (Protocol Registration Receipt NCT03174678) at clinicaltrials.gov.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of dexmedetomidine as a premedication for pediatric patients undergoing outpatient dental surgery under general anaethesia-systematic review and meta-analysis.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 31;13:e19216. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19216. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40183044 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of oral dexmedetomidine and midazolam for premedication and emergence delirium in children after dental procedures under general anesthesia: a retrospective study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Mar 28;12:647-653. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S163828. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29636599 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Intranasal Dexmedetomidine and Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Pediatric Dental Patients under General Anesthesia: A Randomised Clinical Trial.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 24;2020:5142913. doi: 10.1155/2020/5142913. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32382556 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Effects of intranasal dexmedetomidine for children undergoing dental rehabilitation under general anesthesia: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Dec 18;50(6):1078-1082. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30562785 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Efficacy and safety of intranasal dexmedetomidine premedication for children undergoing CT or magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Apr 2;58(4):314-318. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20191224-00830. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32234139 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Sweet-Tasting Ionic Conjugates of Local Anesthetics and Vasoconstrictors.Molecules. 2021 Feb 12;26(4):983. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040983. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33673320 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of midazolam administration for the prevention of emergence agitation in pediatric patients with extreme fear and non-cooperation undergoing dental treatment under sevoflurane anesthesia, a double-blind, randomized study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 May 17;13:1729-1737. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S198123. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31190751 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Publication bias in pediatric emergence delirium: a cross-sectional analysis of ClinicalTrials.gov and ClinicalTrialsRegister.eu.BMJ Open. 2020 Oct 15;10(10):e037346. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037346. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 33060081 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of dexmedetomidine as a premedication for pediatric patients undergoing outpatient dental surgery under general anaethesia-systematic review and meta-analysis.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 31;13:e19216. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19216. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40183044 Free PMC article.
-
Role of dexmedetomidine in pediatric dental sedation.J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2019 Apr;19(2):83-90. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2019.19.2.83. Epub 2019 Apr 30. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2019. PMID: 31065590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schroth R. J., Quiñonez C., Shwart L., Wagar B. Treating early childhood caries under general anesthesia: A national review of Canadian data. Journal of the Canadian Dental Association. 2016;82, article no. g20 - PubMed
-
- Yuki K., Daaboul D. G. Postoperative maladaptive behavioral changes in children. Middle East Journal of Anesthesiology. 2011;21(2):183–192. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical