Foot Structure in Boys with Down Syndrome
- PMID: 28904967
- PMCID: PMC5585551
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7047468
Foot Structure in Boys with Down Syndrome
Abstract
Introduction and aim: Down syndrome (DS) is associated with numerous developmental abnormalities, some of which cause dysfunctions of the posture and the locomotor system. The analysis of selected features of the foot structure in boys with DS versus their peers without developmental disorders is done.
Materials and methods: The podoscopic examination was performed on 30 boys with DS aged 14-15 years. A control group consisted of 30 age- and gender-matched peers without DS.
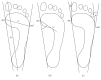
Results: The feet of boys with DS are flatter compared to their healthy peers. The hallux valgus angle is not the most important feature differentiating the shape of the foot in the boys with DS and their healthy peers. In terms of the V toe setting, healthy boys had poorer results.
Conclusions: Specialized therapeutic treatment in individuals with DS should involve exercises to increase the muscle strength around the foot joints, enhancing the stabilization in the joints and proprioception. Introducing orthotics and proper footwear is also important. It is also necessary to monitor the state of the foot in order to modify undertaken therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Lizis P. Formation of Longitudinal Arch of the Foot And Problems of Flat Foot Correction in Children and Adolescents at Developmental Age. Krakow, Poland: AWF; 2000.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

