Misuse of Topical Corticosteroids for Cosmetic Purpose in Antananarivo, Madagascar
- PMID: 28904977
- PMCID: PMC5585578
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9637083
Misuse of Topical Corticosteroids for Cosmetic Purpose in Antananarivo, Madagascar
Abstract
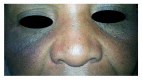
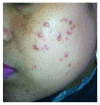
This cross-sectional study was conducted in Antananarivo, Madagascar, from June to September 2012. We aim to evaluate the misuse of TC on the face for cosmetic purpose and the adverse effects due to its application. A questionnaire-based analysis was done among females who use topical corticosteroids on the face for cosmetic purpose. Of the 770 women questioned, 384 (49,8%) used topical corticosteroids for cosmetic purpose whose mean age was 38 years (range 16-73 years). Two hundred and sixty-one females (68%) used TC combined with handcrafted cosmetics, and 123 (32%) used TC alone. "Pandalao," which contains salicylic acid, peppermint oil, lanolin, powder of Juanes de Vigo (mercury powder), and Vaseline, is the most handcrafted cosmetic combined with TC in our study (used by 29,4% respondents). Only one (0,26%) had obtained the TC by physician's prescription, 234 (61%) from cosmetic retailers, 92 (23%) directly from local pharmacies, 49 (12%) from beauticians, and 15 (4%) from unspecified sources. Lightening of skin color was the main reason for using TC in 44,8% of respondents in the absence of any primary dermatosis. Pigmentation disorders (63,2%) and cutaneous atrophy (52,1%) were the most adverse effects noted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Widespread use of toxic skin lightening compounds: medical and psychosocial aspects.Dermatol Clin. 2011 Jan;29(1):111-23. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2010.08.010. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Dermatol Clin. 2011. PMID: 21095535 Review.
-
Impact of Abuse of Topical Corticosteroids and Counterfeit Cosmetic Products for the Face: Prospective Demographic Study in Basrah City, Iraq.Curr Drug Saf. 2020;15(1):25-31. doi: 10.2174/1574886314666191001100357. Curr Drug Saf. 2020. PMID: 31573892
-
Aesthetic problems associated with the cosmetic use of bleaching products.Int J Dermatol. 2007 Oct;46 Suppl 1:15-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2007.03456.x. Int J Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17919199
-
Complications of chronic use of skin lightening cosmetics.Int J Dermatol. 2008 Apr;47(4):344-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2008.02719.x. Int J Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18377596 Review.
-
The widespread use of skin lightening creams in Senegal: a persistent public health problem in West Africa.Int J Dermatol. 2002 Feb;41(2):69-72. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01335.x. Int J Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 11982639
Cited by
-
Attitude Toward Using the Triple Combination Bleaching Formula and Related Outcomes: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2021 Dec 20;13(12):e20542. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20542. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35070569 Free PMC article.
-
Questionnaire-Based Study of 392 Women in Abbottabad, Pakistan, to Evaluate the Types of Cosmetic Products Purchased Between December 2018 and March 2019 and Their Associated Adverse Events.Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2024 Mar 29;30:e943048. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.943048. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2024. PMID: 38549239 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Mercury Exposures from Skin-Lightening Products.Environ Health Perspect. 2022 Nov;130(11):116002. doi: 10.1289/EHP10808. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Environ Health Perspect. 2022. PMID: 36367779 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating quackery formulations: LC-MS/MS based method for detecting glucocorticoid content.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Oct 9;13:101763. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101763. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39497759 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns and Motivations of Topical Steroid Use for Skin Whitening in Jazan, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Survey.Cureus. 2024 Sep 2;16(9):e68455. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68455. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39360113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rindani T. H. Topical action of steroid hormones on inflammation. Archives Internationales De Pharmacodynamie Et De Therapie. 1954;99:467–473. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical