Steer-PROP: a GRASE-PROPELLER sequence with interecho steering gradient pulses
- PMID: 28905474
- PMCID: PMC5821559
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.26898
Steer-PROP: a GRASE-PROPELLER sequence with interecho steering gradient pulses
Abstract
Purpose: This study demonstrates a novel PROPELLER (periodically rotated overlapping parallel lines with enhanced reconstruction) pulse sequence, termed Steer-PROP, based on gradient and spin echo (GRASE), to reduce the imaging times and address phase errors inherent to GRASE. The study also illustrates the feasibility of using Steer-PROP as an alternative to single-shot echo planar imaging (SS-EPI) to produce distortion-free diffusion images in all imaging planes.
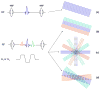
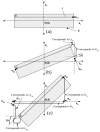
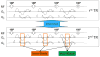
Methods: Steer-PROP uses a series of blip gradient pulses to produce N (N = 3-5) adjacent k-space blades in each repetition time, where N is the number of gradient echoes in a GRASE sequence. This sampling strategy enables a phase correction algorithm to systematically address the GRASE phase errors as well as the motion-induced phase inconsistency. Steer-PROP was evaluated on phantoms and healthy human subjects at both 1.5T and 3.0T for T2 - and diffusion-weighted imaging.
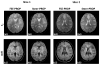
Results: Steer-PROP produced similar image quality as conventional PROPELLER based on fast spin echo (FSE), while taking only a fraction (e.g., 1/3) of the scan time. The robustness against motion in Steer-PROP was comparable to that of FSE-based PROPELLER. Using Steer-PROP, high quality and distortion-free diffusion images were obtained from human subjects in all imaging planes, demonstrating a considerable advantage over SS-EPI.
Conclusion: The proposed Steer-PROP sequence can substantially reduce the scan times compared with FSE-based PROPELLER while achieving adequate image quality. The novel k-space sampling strategy in Steer-PROP not only enables an integrated phase correction method that addresses various sources of phase errors, but also minimizes the echo spacing compared with alternative sampling strategies. Steer-PROP can also be a viable alternative to SS-EPI to decrease image distortion in all imaging planes. Magn Reson Med 79:2533-2541, 2018. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Keywords: GRASE; PROPELLER; Steer-PROP; diffusion imaging; k-space trajectory; phase correction.
© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures



References
-
- Pipe JG. Motion correction with PROPELLER MRI: Application to head motion and free-breathing cardiac imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1999;42(5):963–969. - PubMed
-
- Pipe JG, Farthing VG, Forbes KP. Multishot diffusion-weighted FSE using PROPELLER MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2002;47(1):42–52. - PubMed
-
- Deng J, Larson AC. Modified PROPELLER approach for T2-mapping of the abdomen. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2009;61(6):1269–1278. - PubMed
-
- Hirokawa Y, Isoda H, Maetani YS, Arizono S, Shimada K, Okada T, Shibata T, Togashi K. Hepatic lesions: improved image quality and detection with the periodically rotated overlapping parallel lines with enhanced reconstruction technique--evaluation of SPIO-enhanced T2-weighted MR images. Radiology. 2009;251(2):388–397. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein MA, King KF, Zhou XJ. Handbook of MRI Pulse Sequences. Elsevier Publishing; San Diego, CA: 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

