Salidroside suppressing LPS-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 28905500
- PMCID: PMC5706507
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12871
Salidroside suppressing LPS-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
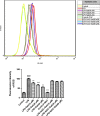
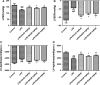
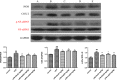
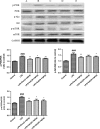
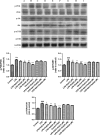
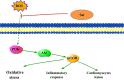
The purpose of the present study was to investigate the effect of salidroside (Sal) on myocardial injury in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxemic in vitro and in vivo. SD rats were randomly divided into five groups: control group, LPS group (15 mg/kg), LPS plus dexamethasone (2 mg/kg), LPS plus Sal groups with different Sal doses (20, 40 mg/kg). Hemodynamic measurement and haematoxylin and eosin staining were performed. Serum levels of creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase, the activities of the antioxidant enzymes catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px), glutathione, tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) were measured after the rats were killed. iNOS, COX-2, NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway proteins were detected by Western blot. In vitro, we evaluated the protective effect of Sal on rat embryonic heart-derived myogenic cell line H9c2 induced by LPS. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in H9c2 cells was measured by flow cytometry, and the activities of the antioxidant enzymes CAT, SOD, GSH-px, glutathione-S-transferase, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in cellular supernatant were measured. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling was examined by Western blot. As a result, Sal significantly attenuated the above indices. In addition, Sal exerts pronounced cardioprotective effect in rats subjected to LPS possibly through inhibiting the iNOS, COX-2, NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in vivo. Furthermore, the pharmacological effect of Sal associated with the ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway was proved by the use of ROS scavenger, N-acetyl-l-cysteine, in LPS-stimulated H9C2 cells. Our results indicated that Sal could be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: LPS; ROS; H9C2; PI3K/Akt/mTOR; myocardial injury; salidroside.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures






References
-
- Zhang T, Yan T, Du J, et al Apigenin attenuates heart injury in lipopolysaccharide‐induced endotoxemic model by suppressing sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine 1‐phosphate signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 2015; 233: 46–55. - PubMed
-
- Jiang W, Luo F, Lu Q, et al The protective effect of Trillin LPS‐induced acute lung injury by the regulations of inflammation and oxidative state. Chem Biol Interact. 2016; 243: 127–34. - PubMed
-
- Chen T, Mou Y, Tan J, et al The protective effect of CDDO‐Me on lipopolysaccharide‐induced acute lung injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015; 25: 55–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

