Plication as an alternative to resection in horizontal strabismus: A randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 28905830
- PMCID: PMC5621269
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_968_16
Plication as an alternative to resection in horizontal strabismus: A randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Purpose: Resections and plications tighten recti although the latter are less traumatic, potentially reversible, quicker, and vascularity preserving. To compare inflammation, scarring, and alignment in horizontal strabismus, operated uniocularly by either resections or plications (with recessions): recession and resection (R&R) or recession and plication (R&P) groups. This was a prospective, patient and assessor blind, randomized trial.
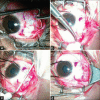
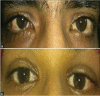
Methods: All consenting strabismus patients qualifying for the first-time uniocular horizontal rectus surgeries underwent detailed ocular examination and were randomized into standard R&R or R&P groups. For the latter, we folded the tendon-muscle strap the desired amount using 6-0 polyglactin, suturing it to its insertion, entailing no disinsertion. We compared the groups for inflammatory grades (individually for congestion, chemosis, discharge, foreign-body sensation, and drop intolerance and aggregated to a total inflammatory score (TIS), scar visibility (SV) at 1 m, and successful alignment (≤10 prism diopter of orthotropia). We used Mann-Whitney and Fisher's exact tests, with significance at P ≤ 0.05.
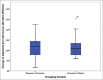
Results: We randomized 40 patients: 22 to R&R and 18 to R&P. The groups were comparable in age, strabismus onset and duration, and strabismus amount. The inflammatory scores, both individual and TIS, were comparable at all time-points: all P > 0.05. SV proportions were not significantly different: 16/22 in R&R versus 9/18 in R&P; P = 0.19. There were no significant differences in success rates: 14/22 versus 10/18, P = 0.74.
Conclusion: Our study shows that plication is similarly effective as resection, when combined with recession in horizontal strabismus, and should be resorted to more frequently.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Plication: How apt in application?Indian J Ophthalmol. 2017 Sep;65(9):785-786. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_702_17. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28905819 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- von Noorden GK. Principles of surgical treatment. In: Lampert R, editor. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility: Theory and Management of Strabismus. 6th ed. St Louis: Mosby; 2002. pp. 566–624.
-
- Nelson BA, Gunton KB, Lasker JN, Nelson LB, Drohan LA. The psychosocial aspects of strabismus in teenagers and adults and the impact of surgical correction. J AAPOS. 2008;12:72–6.e1. - PubMed
-
- Archer SM, Musch DC, Wren PA, Guire KE, Del Monte MA. Social and emotional impact of strabismus surgery on quality of life in children. J AAPOS. 2005;9:148–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

