Triptolide induces Sertoli cell apoptosis in mice via ROS/JNK-dependent activation of the mitochondrial pathway and inhibition of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response
- PMID: 28905938
- PMCID: PMC5800476
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2017.95
Triptolide induces Sertoli cell apoptosis in mice via ROS/JNK-dependent activation of the mitochondrial pathway and inhibition of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response
Abstract
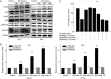
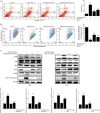
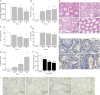
Triptolide (TP), an oxygenated diterpene, has a variety of beneficial pharmacodynamic activities but its clinical applications are restricted due to severe testicular injury. This study aimed to delineate the molecular mechanisms of TP-induced testicular injury in vitro and in vivo. TP (5-50000 nmol/L) dose-dependently decreased the viability of TM4 Sertoli cells with an IC50 value of 669.5-269.45 nmol/L at 24 h. TP (125, 250, and 500 nmol/L) dose-dependently increased the accumulation of ROS, the phosphorylation of JNK, mitochondrial dysfunction and activation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway in TM4 cells. These processes were attenuated by co-treatment with the antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine (NAC, 1 mmol/L). Furthermore, TP treatment inhibited the translocation of Nrf2 from cytoplasm into the nucleus as well as the expression of downstream genes NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase1 (NQO1), catalase (CAT) and hemeoxygenase 1 (HO-1), thus abrogating Nrf2-mediated defense mechanisms against oxidative stress. Moreover, siRNA knockdown of Nrf2 significantly potentiated TP-induced apoptosis of TM4 cells. The above results from in vitro experiments were further validated in male mice after oral administration of TP (30, 60, and 120 mg·kg-1·d-1, for 14 d), as evidenced by the detected indexes, including dose-dependently decreased SDH activity, increased MDA concentration, altered testicle histomorphology, elevated caspase-3 activation, apoptosis induction, increased phosphorylation of JNK, and decreased gene expression of NQO1, CAT and HO-1 as well as nuclear protein expression of Nrf2 in testicular tissue. Our results demonstrate that TP activates apoptosis of Sertoli cells and injury of the testis via the ROS/JNK-mediated mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis pathway and down-regulates Nrf2 activation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Triptolide-induced oxidative stress involved with Nrf2 contribute to cardiomyocyte apoptosis through mitochondrial dependent pathways.Toxicol Lett. 2014 Nov 4;230(3):454-66. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.08.017. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Toxicol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25169008
-
Aucubin, a natural iridoid glucoside, attenuates oxidative stress-induced testis injury by inhibiting JNK and CHOP activation via Nrf2 up-regulation.Phytomedicine. 2019 Nov;64:153057. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153057. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31419730
-
Luteolin Ameliorates Testis Injury and Blood-Testis Barrier Disruption through the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and by Upregulating Cx43.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019 May;63(10):e1800843. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201800843. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019. PMID: 30924608
-
[Triptolide induces oxidative stress and apoptosis and activates PIK3/Akt signaling pathway in TM4 sertoli cells].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Aug 18;50(4):607-612. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30122757 Chinese.
-
Self-protection against triptolide-induced toxicity in human hepatic cells via Nrf2-ARE-NQO1 pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Dec;23(12):929-936. doi: 10.1007/s11655-017-2546-6. Epub 2017 May 18. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 28523535
Cited by
-
Triptolide Causes Spermatogenic Disorders by Inducing Apoptosis in the Mitochondrial Pathway of Mouse Testicular Spermatocytes.Toxics. 2024 Dec 10;12(12):896. doi: 10.3390/toxics12120896. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39771111 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of mitochondria in the pharmacological and toxicological effects of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F: functions, targets and new therapeutic applications.Chin Med. 2025 Jul 16;20(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01170-6. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40671123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of the mechanism for the combination of diallyl trisulfide and cisplatin against gastric cancer: a network pharmacology study and pharmacological evaluation.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 30;14:1269895. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1269895. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37964870 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of a combination of triptolide and ferulic acid on the activities of CYP450 enzymes and oxidative stress in HaCaT cells.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Dec;20(6):157. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9286. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 33093895 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally occurring anti-cancer compounds: shining from Chinese herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2019 Nov 6;14:48. doi: 10.1186/s13020-019-0270-9. eCollection 2019. Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31719837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lu Y, Bao X, Sun T, Xu J, Zheng W, Shen P. Triptolide attenuate the oxidative stress induced by LPS/D-GalN in mice. J Cell Biochem 2012; 113: 1022–33. - PubMed
-
- Fu Q, Jiang ZZ, Zhang LY. Impairment of triptolide on liver mitochondria in isolated liver mitochondria and HL7702 cell line. Chin J Integr Med 2013; 19: 683–8. - PubMed
-
- Kupchan SM, Court WA, Dailey RG Jr, Gilmore CJ, Bryan RF. Triptolide and tripdiolide, novel antileukemic diterpenoid triepoxides from Tripterygium wilfordii. J Am Chem Soc 1972; 94: 7194–5. - PubMed
-
- Wang B, Ma L, Tao X, Lipsky PE. Triptolide, an active component of the Chinese herbal remedy Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F, inhibits production of nitric oxide by decreasing inducible nitric oxide synthase gene transcription. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: 2995–303. - PubMed
-
- Lin N, Sato T, Ito A. Triptolide, a novel diterpenoid triepoxide from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f., suppresses the production and gene expression of pro-matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 3 and augments those of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1 and 2 in human synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 2001; 44: 2193–200. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

