Reflux episodes and esophageal impedance levels in patients with typical and atypical symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease
- PMID: 28906377
- PMCID: PMC5604646
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007978
Reflux episodes and esophageal impedance levels in patients with typical and atypical symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease
Abstract
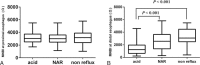
To determine the relationship between baseline impedance levels and gastroesophageal reflux, we retrospectively enrolled 110 patients (54 men and 56 female; mean age, 51 ± 14 years) with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) who underwent 24-h multichannel intraluminal impedance and pH monitoring. Patients were stratified according to symptom (typical or atypical) and reflux types (acid reflux, nonacid reflux [NAR], or no abnormal reflux). Mean nocturnal baseline impedance (MNBI) were measured 3 cm (distal esophagus) and 17 cm (proximal esophagus) above the lower esophageal sphincter. Median distal esophageal MNBI was lower in the acid reflux group (1244 Ω; 647-1969 Ω) than in the NAR (2586 Ω; 1368-3666 Ω) or no abnormal reflux groups (3082 Ω; 2495-4472 Ω; all P < .05). Distal MNBI were negatively correlated with DeMeester score and acid exposure time. Atypical symptoms were more frequently associated with NAR than typical symptoms (P < .01). Among patients with positive symptom-association probability (SAP) for NAR, median proximal MNBI tended to be lower in patients with typical symptoms (median, 3013 Ω; IQR, 2535-3410 Ω) than in those with atypical symptoms (median, 3386 Ω; IQR, 3044-3730 Ω, P = .05). Thus, atypical GERD symptoms were more likely to be associated with NAR. The mucosal integrity of the proximal esophagus might be relatively impaired in GERD patients with typical symptoms for NAR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mean nocturnal baseline impedance: Influencing factors and diagnostic value in gastroesophageal reflux disease.Technol Health Care. 2023;31(5):1875-1886. doi: 10.3233/THC-220814. Technol Health Care. 2023. PMID: 36970927
-
Mean Nocturnal Baseline Impedance May Be Greater Than 2500 Ohms in Chinese Patients With GERD.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2025 Feb;37(2):e14986. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14986. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2025. PMID: 39739307
-
COMBINED 24-HOURS ESOPHAGEAL PH MONITORING AND MULTICHANNEL INTRALUMINAL IMPEDANCE FOR COMPARISON OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX IN CHILDREN WITH TYPICAL VERSUS ATYPICAL SYMPTOMS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE.Arq Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul-Sep;53(3):130-5. doi: 10.1590/S0004-28032016000300002. Arq Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27438415
-
Mean nocturnal baseline impedance, a novel metric of multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring in diagnosing gastroesophageal reflux disease.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 11;15:17562848221105195. doi: 10.1177/17562848221105195. eCollection 2022. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35983222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mucosal impedance as a diagnostic tool for gastroesophageal reflux disease: an update for clinicians.Dis Esophagus. 2024 Aug 29;37(9):doae037. doi: 10.1093/dote/doae037. Dis Esophagus. 2024. PMID: 38670809 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can Esophageal Baseline Impedance Predict Proton Pump Inhibitor Response in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018 Jan 30;24(1):1-3. doi: 10.5056/jnm17138. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018. PMID: 29291602 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sex-Based Differences in pH Parameters and Esophageal Impedance of Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 May 28;8:629302. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.629302. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34124085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, et al. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global, evidence-based consensus paper. Z Gastroenterol 2007;45:1125–40. - PubMed
-
- Sidhwa F, Moore A, Alligood E, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of the extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 2016;265:63–7. - PubMed
-
- Futagami S, Iwakiri K, Shindo T, et al. The prokinetic effect of mosapride citrate combined with omeprazole therapy improves clinical symptoms and gastric emptying in PPI-resistant NERD patients with delayed gastric emptying. J Gastroenterol 2010;45:413–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

