The role of serum angiopoietin-2 levels in progression and prognosis of lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 28906403
- PMCID: PMC5604672
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008063
The role of serum angiopoietin-2 levels in progression and prognosis of lung cancer: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis is an essential process in the development and progression of malignant tumors including lung cancer, in which angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) plays an important role. The objective of this study was to assess the prognostic value of serum Ang-2 levels in patients with lung cancer.
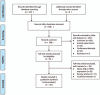
Methods: A comprehensive systematic electronic search was performed in the Pubmed, Embase, Web of Science, china national knowledge infrastructure, and VIP databases update to October, 2016 (qikan.cqvip.com). Literatures examining the relevance of serum Ang-2 levels to progression and prognosis of lung cancer were eligible for our study. Standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and a P value were applied to compare continuous variables, and hazard ratio (HR) with 95% CI as well as P value were applied for prognostic role.
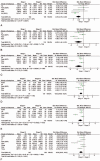
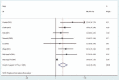
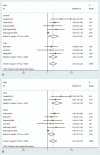
Results: Twenty studies with 1911 patients met the eligibility criteria. Among them, 7 studies with 575 patients with lung cancer assessed the association between expression of serum Ang-2 and prognosis. According to our results, higher levels of serum Ang-2 were associated with the later stage of tumor. Serum Ang-2 levels were significantly lower in stage I than in stage II (SMD: -0.51; 95% CI: -0.75 to -0.27; P < .001), in stage II than in stage III (SMD: -0.52; 95% CI: -0.80 to -0.24; P < .001), in stage III than in stage IV (SMD: -0.58; 95% CI: -0.93 to -0.23; P = .001). In addition, serum Ang-2 levels were higher in patients with lymph node metastasis (SMD: 1.06; 95% CI, 0.57-1.56; P < .001). Meanwhile, patients with lung cancer with higher levels of serum Ang-2 were associated with a significant poorer prognosis when compared to those with lower serum Ang-2 levels (HR: 1.64; 95% CI: 1.20-2.25; P = .002), and this role was further detected when stratified by ethnicity and histological type.
Conclusions: This systematic review and meta-analysis suggested that serum Ang-2 levels might be a potential predictor for staging, and were associated with prognosis of lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Figures
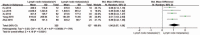
Similar articles
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative angiopoietin-2 serum levels: a marker of malignant potential in ovarian neoplasms and poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010 Dec;20(9):1498-505. doi: 10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181f936e3. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21119365
-
Gestational weight gain below instead of within the guidelines per class of maternal obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of obstetrical and neonatal outcomes.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022 Sep;4(5):100682. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2022.100682. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022. PMID: 35728780
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Baseline Ang-2 Serum Levels as a Predictive Factor for Survival in NSCLC and SCLC.Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 13;12(12):2092. doi: 10.3390/life12122092. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556457 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Dynamics of Coagulation and Angiogenesis Markers in Cancer Patients During and After Chemotherapy.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021 Jan-Dec;27:10760296211056637. doi: 10.1177/10760296211056637. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2021. PMID: 34918975 Free PMC article.
-
A Unified Transcriptional, Pharmacogenomic, and Gene Dependency Approach to Decipher the Biology, Diagnostic Markers, and Therapeutic Targets Associated with Prostate Cancer Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 14;13(20):5158. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205158. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680307 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-145-5p suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer epithelial cells via the ANGPT2/NOD_LIKE_RECEPTOR axis.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Aug 28;20:416. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01483-6. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32874130 Free PMC article.
-
Angiopoietin 2 as a Novel Potential Biomarker for Acute Aortic Dissection.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Dec 23;8:743519. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.743519. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 35004874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2016;11:39–51. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J, Watson K, Ingiber D, et al. Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature 1989;339:58–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

