Differences in clinical features observed between childhood-onset versus adult-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28906413
- PMCID: PMC5604682
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008086
Differences in clinical features observed between childhood-onset versus adult-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) affects people in childhood (childhood onset) or in adulthood (adult onset). Observational studies that have previously compared childhood-onset versus adult-onset SLE were often restricted to 1 ethnic group, or to a particular area, with a small sample size of patients. We aimed to systematically compare childhood-onset versus adult-onset SLE through a meta-analysis.
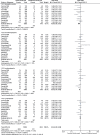
Methods: Electronic databases were searched for relevant publications comparing childhood-onset with adult-onset SLE. Adverse clinical features were considered as the endpoints. The Newcastle Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used to assess the methodological quality of the studies and RevMan software (version 5.3) was used to carry out this analysis whereby risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) were used as the statistical parameters.
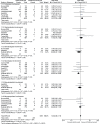
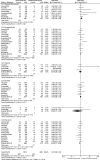
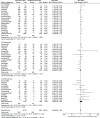
Results: A total number of 10,261 participants (1560 participants with childhood-onset SLE and 8701 participants with adult-onset SLE) were enrolled. Results of this analysis showed that compared with childhood-onset SLE, pulmonary involvement was significantly higher with adult-onset SLE (RR: 1.51, 95% CI: 1.18-1.93; P = .001), whereas renal involvement was significantly higher with childhood-onset SLE (RR: 0.65, 95% CI: 0.55-0.77; P = .00001). Raynaud phenomenon and photosensitivity were significantly higher in adult-onset SLE (RR: 1.29, 95% CI: 1.04-1.60; P = .02) and (RR: 1.08, 95% CI: 1.01-1.17; P = .03), respectively. Malar rash significantly favored adult-onset SLE (RR: 0.84, 95% CI: 0.75-0.94; P = .002). Childhood-onset SLE was associated with significantly higher hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukocytopenia, and lymphopenia. Seizure and ocular manifestations were significantly higher with childhood-onset SLE (RR: 0.57, 95% CI: 0.47-0.70; P = .00001) and (RR: 0.34, 95% CI: 0.21-0.55; P = .00001), respectively, whereas pleuritis was significantly higher with adult-onset SLE (RR: 1.45, 95% CI: 1.17-1.79; P = .0008). Vasculitis and fever were significantly higher with childhood-onset SLE (RR: 0.51, 95% CI: 0.36-0.74; P = .0004) and (RR: 0.78, 95% CI: 0.68-0.89; P = .0002) respectively.
Conclusion: Significant differences were observed between childhood-onset versus adult-onset SLE, showing the former to be more aggressive.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Tiao J, Feng R, Carr K, et al. Using the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) criteria to determine the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in patients with subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE). J Am Acad Dermatol 2016;74:862–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Budhoo A, Mody GM, Dubula T, et al. Comparison of ethnicity, gender, age of onset and outcome in South Africans with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2017;26:438–46. - PubMed
-
- Nikpour M, Bridge JA, Richter S. A systematic review of prevalence, disease characteristics and management of systemic lupus erythematosus in Australia: identifying areas of unmet need. Intern Med J 2014;44:1170–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

