Identification of transforming growth factor-beta-regulated microRNAs and the microRNA-targetomes in primary lung fibroblasts
- PMID: 28910321
- PMCID: PMC5599028
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183815
Identification of transforming growth factor-beta-regulated microRNAs and the microRNA-targetomes in primary lung fibroblasts
Abstract
Background: Lung fibroblasts are involved in extracellular matrix homeostasis, which is mainly regulated by transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), and are therefore crucial in lung tissue repair and remodeling. Abnormal repair and remodeling has been observed in lung diseases like COPD. As miRNA levels can be influenced by TGF-β, we hypothesized that TGF-β influences miRNA expression in lung fibroblasts, thereby affecting their function.
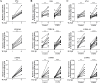
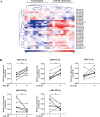
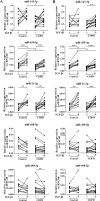
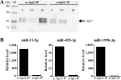
Materials and methods: We investigated TGF-β1-induced miRNA expression changes in 9 control primary parenchymal lung fibroblasts using miRNA arrays. TGF-β1-induced miRNA expression changes were validated and replicated in an independent set of lung fibroblasts composted of 10 controls and 15 COPD patients using qRT-PCR. Ago2-immunoprecipitation followed by mRNA expression profiling was used to identify the miRNA-targetomes of unstimulated and TGF-β1-stimulated primary lung fibroblasts (n = 2). The genes affected by TGF-β1-modulated miRNAs were identified by comparing the miRNA targetomes of unstimulated and TGF-β1-stimulated fibroblasts.
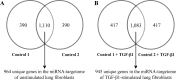
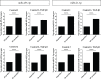
Results: Twenty-nine miRNAs were significantly differentially expressed after TGF-β1 stimulation (FDR<0.05). The TGF-β1-induced miR-455-3p and miR-21-3p expression changes were validated and replicated, with in addition, lower miR-455-3p levels in COPD (p<0.05). We identified 964 and 945 genes in the miRNA-targetomes of unstimulated and TGF-β1-stimulated lung fibroblasts, respectively. The TGF-β and Wnt pathways were significantly enriched among the Ago2-IP enriched and predicted targets of miR-455-3p and miR-21-3p. The miR-455-3p target genes HN1, NGF, STRADB, DLD and ANO3 and the miR-21-3p target genes HHEX, CHORDC1 and ZBTB49 were consistently more enriched after TGF-β1 stimulation.
Conclusion: Two miRNAs, miR-455-3p and miR-21-3p, were induced by TGF-β1 in lung fibroblasts. The significant Ago2-IP enrichment of targets of these miRNAs related to the TGF-β and/or Wnt pathways (NGF, DLD, HHEX) in TGF-β1-stimulated fibroblasts suggest a role for these miRNAs in lung diseases by affecting lung fibroblast function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Marked TGF-β-regulated miRNA expression changes in both COPD and control lung fibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 3;9(1):18214. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54728-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31796837 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression networks in COPD: microRNA and mRNA regulation.Thorax. 2012 Feb;67(2):122-31. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200089. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Thorax. 2012. PMID: 21940491
-
Identifying microRNAs targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in end-stage idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Mol Med (Berl). 2016 Aug;94(8):875-85. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1426-z. Epub 2016 May 18. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27188753 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
MicroRNA Expression Profiles, Target Genes, and Pathways in Intervertebral Disk Degeneration: A Meta-Analysis of 3 Microarray Studies.World Neurosurg. 2019 Jun;126:389-397. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.03.120. Epub 2019 Mar 20. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 30904808 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-378 associated with proliferation, migration and apoptosis properties in A549 cells and targeted NPNT in COPD.PeerJ. 2022 Sep 15;10:e14062. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14062. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36128198 Free PMC article.
-
Parentage testing and looking for single nucleotide markers associated with antler quality in deer (Cervus elaphus).Arch Anim Breed. 2022 Jul 28;65(3):267-274. doi: 10.5194/aab-65-267-2022. eCollection 2022. Arch Anim Breed. 2022. PMID: 36035877 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve Growth Factor: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Lung Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 24;22(17):9112. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179112. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homeobox protein Hhex negatively regulates Treg cells by inhibiting Foxp3 expression and function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 17;116(51):25790-25799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907224116. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31792183 Free PMC article.
-
Marked TGF-β-regulated miRNA expression changes in both COPD and control lung fibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 3;9(1):18214. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54728-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31796837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brandsma CA, van den Berge M, Postma DS, Jonker MR, Brouwer S, Pare PD, et al. A large lung gene expression study identifying fibulin-5 as a novel player in tissue repair in COPD. Thorax. 2015;70(1):21–32. Epub 2014/07/06. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-205091 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Renzoni EA, Abraham DJ, Howat S, Shi-Wen X, Sestini P, Bou-Gharios G, et al. Gene expression profiling reveals novel TGFbeta targets in adult lung fibroblasts. Respiratory research. 2004;5:24 Epub 2004/12/02. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-5-24 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC538264. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zandvoort A, Postma DS, Jonker MR, Noordhoek JA, Vos JT, Timens W. Smad gene expression in pulmonary fibroblasts: indications for defective ECM repair in COPD. Respiratory research. 2008;9:83 Epub 2008/12/18. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-9-83 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2613883. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eickelberg O, Kohler E, Reichenberger F, Bertschin S, Woodtli T, Erne P, et al. Extracellular matrix deposition by primary human lung fibroblasts in response to TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta3. The American journal of physiology. 1999;276(5 Pt 1):L814–24. Epub 1999/05/18. . - PubMed
-
- Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome research. 2009;19(1):92–105. Epub 2008/10/29. doi: 10.1101/gr.082701.108 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2612969. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

