Transcriptional responses in the hepatopancreas of Eriocheir sinensis exposed to deltamethrin
- PMID: 28910412
- PMCID: PMC5599000
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184581
Transcriptional responses in the hepatopancreas of Eriocheir sinensis exposed to deltamethrin
Abstract
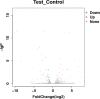
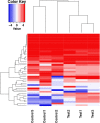
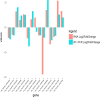
Deltamethrin is an important pesticide widely used against ectoparasites. Deltamethrin contamination has resulted in a threat to the healthy breeding of the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. In this study, we investigated transcriptional responses in the hepatopancreas of E. sinensis exposed to deltamethrin. We obtained 99,087,448, 89,086,478, and 100,117,958 raw sequence reads from control 1, control 2, and control 3 groups, and 92,094,972, 92,883,894, and 92,500,828 raw sequence reads from test 1, test 2, and test 3 groups, respectively. After filtering and quality checking of the raw sequence reads, our analysis yielded 79,228,354, 72,336,470, 81,859,826, 77,649,400, 77,194,276, and 75,697,016 clean reads with a mean length of 150 bp from the control and test groups. After deltamethrin treatment, a total of 160 and 167 genes were significantly upregulated and downregulated, respectively. Gene ontology terms "biological process," "cellular component," and "molecular function" were enriched with respect to cell killing, cellular process, other organism part, cell part, binding, and catalytic. Pathway analysis using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes showed that the metabolic pathways were significantly enriched. We found that the CYP450 enzyme system, carboxylesterase, glutathione-S-transferase, and material (including carbohydrate, lipid, protein, and other substances) metabolism played important roles in the metabolism of deltamethrin in the hepatopancreas of E. sinensis. This study revealed differentially expressed genes related to insecticide metabolism and detoxification in E. sinensis for the first time and will help in understanding the toxicity and molecular metabolic mechanisms of deltamethrin in E. sinensis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Velísek J, Jurcíková J, Dobsíková R, Svobodová Z, Piacková V, Máchová J, et al. Effects of deltamethrin on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007; 23(3): 297–301. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2006.11.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Milam CD, Farris JL, Wilhide JD. Evaluating mosquito control pesticides for effect on target and nontarget organisms. Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000; 39(3): 324–328. - PubMed
-
- Parvez S, Raisuddin S. Copper modulates non-enzymatic antioxidants in the freshwater fish Channa punctata (Bloch) exposed to deltamethrin. Chamosphere. 2006; 62(8): 1324–1332. - PubMed
-
- Prasanthi K, Muralidhara, Rajini PS. Fenvalerate-induced oxidative damage in rat tissues and its attenuation by dietary sesame oil. Food Chem Toxicol. 2005; 43(2): 299–306. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury SP, Coats JR. Comparative toxicology of the pyrethroid insecticides. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 1989; 108(1): 133–177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

