Safety and immunogenicity of the killed bivalent (O1 and O139) whole-cell cholera vaccine in the Philippines
- PMID: 28910563
- PMCID: PMC5975480
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2017.1342908
Safety and immunogenicity of the killed bivalent (O1 and O139) whole-cell cholera vaccine in the Philippines
Abstract
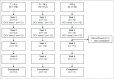
The killed bivalent (O1 and O139) whole cell oral cholera vaccine (OCV) (Shanchol™) was first licensed in India in 2009 and World Health Organization pre-qualified in 2011. We assessed the safety and immunogenicity of this OCV in the Philippines. This was a phase IV, single-arm, descriptive, open-label study. We recruited 336 participants from 2 centers: 112 participants in each age group (1-4, 5-14 and ≥ 15 years). Participants received 2 OCV doses 14 d apart. Safety was monitored throughout the trial. Blood samples were collected at baseline (pre-vaccination) and 14 d after each dose. Serum vibriocidal antibody titers to V. cholerae O1 (El Tor Inaba and El Tor Ogawa) and O139 strains were assessed, with seroconversion defined as ≥ 4-fold increase from baseline in titers. No immediate unsolicited systemic adverse events/reactions were observed. Unsolicited systemic adverse events were mostly grade 1 intensity. One serious adverse event occurred after the first dose, but was unrelated to vaccination. High seroconversion rates (range 69-92%) were achieved against the O1 serotypes with a trend toward higher rates in the 1-4 y (86-92%) and 5-14 y (86-88%) age groups than the ≥ 15 y age group (69-83%). Lower seroconversion rates were achieved against the O139 serotype (35-70%), particularly in those aged ≥ 15 y (35-42%). The 2-dose regimen of the killed bivalent whole cell OCV was well-tolerated in this study conducted in the Philippines, a cholera-endemic country. Robust immune responses were observed even after a single-dose.
Keywords: Shanchol; The Philippines; cholera vaccine; immunogenicity; safety.
Figures

References
-
- Kanungo S, Paisley A, Lopez AL, Bhattacharya M, Manna B, Kim DR, Han SH, Attridge S, Carbis R, Rao R, et al.. Immune responses following one and two doses of the reformulated, bivalent, killed, whole-cell, oral cholera vaccine among adults and children in Kolkata, India: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Vaccine. 2009;27:6887-93. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.09.008. PMID:19761838 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sur D, Kanungo S, Sah B, Manna B, Ali M, Paisley AM, Niyogi SK, Park JK, Sarkar B, Puri MK, et al.. Efficacy of a low-cost, inactivated whole-cell oral cholera vaccine: results from 3 years of follow-up of a randomized, controlled trial. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011;5:e1289. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001289. PMID:22028938 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
