A biologically conjugated polysaccharide vaccine delivered by attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium provides protection against challenge of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O1 infection
- PMID: 28911037
- PMCID: PMC5827577
- DOI: 10.1093/femspd/ftx102
A biologically conjugated polysaccharide vaccine delivered by attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium provides protection against challenge of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O1 infection
Abstract
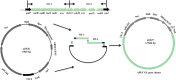
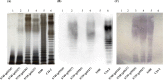
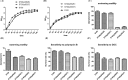
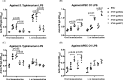
Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) causes avian airsacculitis and colibacillosis, resulting in significant economic loss to the poultry industry. O1, O2 and O78 are the three predominant serotypes. O-antigen of lipopolysaccharide is serotype determinant and highly immunogenic, and O-antigen polysaccharide-based vaccines have great potential for preventing bacterial infections. In this study, we utilized a novel yeast/bacterial shuttle vector pSS26 to clone the 10.8 kb operon synthesizing APEC O1 O-antigen polysaccharide. The resulting plasmid was introduced into attenuated Salmonella vaccines to deliver this O-antigen polysaccharide. O1 O-antigen was stably synthesized in attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium, demonstrated by slide agglutination, silver staining and western blot. Our results also showed that APEC O1 O-antigen produced in the Salmonella vaccines was attached to bacterial cell surfaces, and the presence of heterologous O-antigen did not alter the resistance to surface-acting agents. Furthermore, birds immunized orally or intramuscularly provided protection against the virulent O1 APEC challenge. Salmonella vaccines carrying APEC O1 O-antigen gene cluster also induced high IgG and IgA immune responses against lipopolysaccharide from the APEC O1 strain. The use of our novel shuttle vector facilitates cloning of large DNA fragments, and this strategy could pave the way for production of Salmonella-vectored vaccines against prevalent APEC serotypes.
Keywords: APEC O1; O-antigen polysaccharide; Salmonella Typhimurium; shuttle vector; yeast recombination.
© FEMS 2017. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed A, Li J, Shiloach Y et al. Safety and immunogenicity of Escherichia coli O157 O-specific polysaccharide conjugate vaccine in 2–5-year-old children. J Infect Dis 2006;193:515–21. - PubMed
-
- Attridge SR, Daniels D, Morona JK et al. Surface co-expression of Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella typhi O-antigens on Ty21a clone EX210. Microb Pathog 1990;8:177–88. - PubMed
-
- Bridge DR, Whitmire JM, Makobongo MO et al. Heterologous Pseudomonas aeruginosa O-antigen delivery using a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium wecA mutant strain. Int J Med Microbiol 2016;306:529–40. - PubMed
-
- Cheminay C, Hensel M. Rational design of Salmonella recombinant vaccines. Int J Med Microbiol 2008;298:87–98. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

