Concurrent and sequential initiation of ovarian function suppression with chemotherapy in premenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: an exploratory analysis of TEXT and SOFT
- PMID: 28911092
- PMCID: PMC5834112
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdx285
Concurrent and sequential initiation of ovarian function suppression with chemotherapy in premenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: an exploratory analysis of TEXT and SOFT
Abstract
Background: Recent breast cancer treatment guidelines recommend that higher-risk premenopausal patients should receive ovarian function suppression (OFS) as part of adjuvant endocrine therapy. If chemotherapy is also given, it is uncertain whether to select concurrent or sequential OFS initiation.
Design and methods: We analyzed 1872 patients enrolled in the randomized phase III TEXT and SOFT trials who received adjuvant chemotherapy for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer and upon randomization to an OFS-containing adjuvant endocrine therapy, initiated gonadotropin-releasing-hormone-agonist triptorelin. Breast cancer-free interval (BCFI) was compared between patients who received OFS concurrently with chemotherapy in TEXT (n = 1242) versus sequentially post-chemotherapy in SOFT (n = 630). Because timing of trial enrollment relative to adjuvant chemotherapy differed, we implemented landmark analysis re-defining BCFI beginning 1 year after final dose of chemotherapy (median, 15.5 and 8.1 months from enrollment to landmark in TEXT and SOFT, respectively). As a non-randomized treatment comparison, we implemented comparative-effectiveness propensity score methodology with weighted Cox modeling.
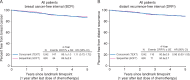
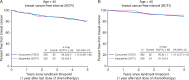
Results: Distributions of several clinico-pathologic characteristics differed between groups. Patients who were premenopausal post-chemotherapy in SOFT were younger on average. The median duration of adjuvant chemotherapy was 18 weeks in both groups. There were 231 (12%) BC events after post-landmark median follow-up of about 5 years. Concurrent use of triptorelin with chemotherapy was not associated with a significant difference in post-landmark BCFI compared with sequential triptorelin post-chemotherapy, either in the overall population (HR = 1.11, 95% CI 0.72-1.72; P = 0.72; 4-year BCFI 89% in both groups), or in the subgroup of 692 women <40 years at diagnosis (HR = 1.13, 95% CI 0.69-1.84) who are less likely to develop chemotherapy-induced amenorrhea.
Conclusion: Based on comparative-effectiveness modeling of TEXT and SOFT after about 5 years median follow-up, with limited statistical power especially for the subgroup <40 years, neither detrimental nor beneficial effect of concurrent administration of OFS with chemotherapy on the efficacy of adjuvant therapy that includes chemotherapy was detected.
Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT00066690 and NCT00066703.
Keywords: GnRH-agonist; adjuvant therapy; hormone receptor-positive; ovarian function suppression; premenopausal; triptorelin.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjuvant treatment of premenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer: design of the TEXT and SOFT trials.Breast. 2013 Dec;22(6):1094-100. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Breast. 2013. PMID: 24095609 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ovarian suppression for adjuvant treatment of hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 6;3(3):CD013538. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013538. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32141074 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-reported outcomes with adjuvant exemestane versus tamoxifen in premenopausal women with early breast cancer undergoing ovarian suppression (TEXT and SOFT): a combined analysis of two phase 3 randomised trials.Lancet Oncol. 2015 Jul;16(7):848-58. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00049-2. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Lancet Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26092816 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Absolute Improvements in Freedom From Distant Recurrence to Tailor Adjuvant Endocrine Therapies for Premenopausal Women: Results From TEXT and SOFT.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Apr 20;38(12):1293-1303. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01967. Epub 2019 Oct 16. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31618131 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with hormone-responsive breast cancer.Breast. 2015 Nov;24 Suppl 2:S120-5. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2015.07.027. Breast. 2015. PMID: 26255743 Review.
Cited by
-
Gender-specific aspects related to type of fertility preservation strategies and access to fertility care.ESMO Open. 2020 Oct;5(Suppl 4):e000771. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2020-000771. ESMO Open. 2020. PMID: 33115753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adjuvant gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian failure in premenopausal women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 3;3(3):CD008018. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008018.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30827035 Free PMC article.
-
Controversies in oncology: which adjuvant endocrine therapy is to be given to premenopausal patients with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer?ESMO Open. 2018 Mar 29;3(3):e000350. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2018-000350. eCollection 2018. ESMO Open. 2018. PMID: 29636992 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sequential versus concurrent adjuvant chemo-endocrine therapy for HR+ early breast cancer: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis.Transl Breast Cancer Res. 2022 Jan 31;3:8. doi: 10.21037/tbcr-21-3. eCollection 2022. Transl Breast Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 38751511 Free PMC article.
-
Metronomic Capecitabine Plus Aromatase Inhibitor as Initial Therapy in Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: The Phase III MECCA Trial.J Clin Oncol. 2025 Apr 10;43(11):1314-1324. doi: 10.1200/JCO.24.00938. Epub 2025 Jan 2. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39746176 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- LHRH-Agonists in Early Breast Cancer Overview Group. Use of luteinising-hormone-releasing hormone agonists as adjuvant treatment in premenopausal patients with hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised adjuvant trials. Lancet 2007; 369: 1711–1723. - PubMed
-
- Fornier MN, Modi S, Panageas KS. et al. Incidence of chemotherapy-induced, long-term amenorrhea in patients with breast carcinoma age 40 years and younger after adjuvant anthracycline and taxane. Cancer 2005; 104: 1575–1579. - PubMed
-
- Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, Yothers G. et al. Adjuvant therapy for very young women with breast cancer: need for tailored treatments. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 2001; 44–51. - PubMed
-
- Aebi S, Gelber S, Castiglione-Gertsch M. et al. Is chemotherapy alone adequate for young women with oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer? Lancet 2000; 355: 1869–1874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

