Biopharmaceutical potentials of Prosopis spp. (Mimosaceae, Leguminosa)
- PMID: 28911536
- PMCID: PMC9333427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2016.11.001
Biopharmaceutical potentials of Prosopis spp. (Mimosaceae, Leguminosa)
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Biopharmaceutical potentials of Prosopis spp. (Mimosaceae, Leguminosa)" [J Food Drug Anal 25 (2017) 187-196].J Food Drug Anal. 2017 Jul;25(3):748-749. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jul 7. J Food Drug Anal. 2017. PMID: 28911661 No abstract available.
Abstract
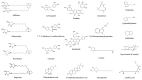
Prosopis is a commercially important plant genus, which has been used since ancient times, particularly for medicinal purposes. Traditionally, Paste, gum, and smoke from leaves and pods are applied for anticancer, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial purposes. Components of Prosopis such as flavonoids, tannins, alkaloids, quinones, or phenolic compounds demonstrate potentials in various biofunctions, such as analgesic, anthelmintic, antibiotic, antiemetic, microbial antioxidant, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antipustule, and antiulcer activities; enhancement of H+, K+, ATPases; oral disinfection; and probiotic and nutritional effects; as well as in other biopharmaceutical applications, such as binding abilities for tablet production. The compound juliflorine provides a cure in Alzheimer disease by inhibiting acetylcholine esterase at cholinergic brain synapses. Some indirect medicinal applications of Prosopis spp. are indicated, including antimosquito larvicidal activity, chemical synthesis by associated fungal or bacterial symbionts, cyanobacterial degradation products, "mesquite" honey and pollens with high antioxidant activity, etc. This review will reveal the origins, distribution, folk uses, chemical components, biological functions, and applications of different representatives of Prosopis.
Keywords: Prosopis; medicinal application; natural product; secondary metabolite.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nadkarni KM, Nadkarni AK. Dr K.M Nadkarni’s Indian materia medica: with Ayurvedic, Unani-tibbi, Siddha, allopathic, homeopathic, naturopathic & home remedies, appendices & indexes. Bombay: Popular Prakashan; 1976.
-
- Mwangi E, Swallow B. Prosopis juliflora invasion and rural livelihoods in the lake Baringo area of Kenya. Conserv Soc. 2008;2:130–40.
-
- Pasiecznik NM, Felker P, Harris PJC, Harsh LN, Cruz G, Tewari JC, Maldonado LJ. The Prosopis juliflora–Prosopis pallida complex: a monograph. Coventry, UK: HDRA; 2001.
-
- Vilela A, Bolkovic ML, Carmanchahi P, Cony M, de Lamo D. Past, present and potential uses of native flora and wildlife of the Monte Desert Wassnerg. J Arid Environ. 2009;73:238–43.
-
- Tapia A, Egly Feresin G, Bustos D, Astudillo L, Theoduloz C, Schmeda-Hirschmann G. Biologically active alkaloids and a free radical scavenger from Prosopis species. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000;71:241–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous