Microencapsulation of fish oil using supercritical antisolvent process
- PMID: 28911651
- PMCID: PMC9328829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2016.11.017
Microencapsulation of fish oil using supercritical antisolvent process
Abstract
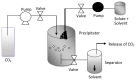
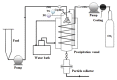
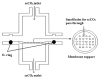
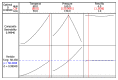
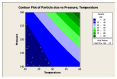
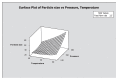
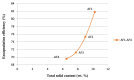
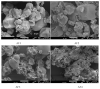
In order to improve the encapsulation process, a newly supercritical antisolvent process was developed to encapsulate fish oil using hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose as a polymer. Three factors, namely, temperature, pressure, and feed emulsion rate were optimized using response surface methodology. The suitability of the model for predicting the optimum response value was evaluated at the conditions of temperature at 60°C, pressure at 150 bar, and feed rate at 1.36 mL/min. At the optimum conditions, particle size of 58.35 μm was obtained. The surface morphology of the micronized fish oil was also evaluated using field emission scanning electron microscopy where it showed that particles formed spherical structures with no internal voids. Moreover, in vitro release of oil showed that there are significant differences of release percentage of oil between the formulations and the results proved that there was a significant decrease in the in vitro release of oil from the powder when the polymer concentration was high.
Keywords: HPMC; microencapsulation; omega 3; supercritical antisolvent.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All contributing authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stone NJ. Fish consumption, fish oil, lipids, and coronary heart disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997;65:1083–6. - PubMed
-
- Salem N, Simopoulos AP, Galli C, Lagarde M, Knapp H. Proc. 2nd Congr ISSFAL on fatty acids and lipids from cell biology to human disease. Lipids. 1998;31(Suppl 1):11–32.
-
- Simopoulos AP, Leaf A, Salem N., Jr Essentiality of and recommended dietary intakes for omega-6 andomega-3 fatty acids. Ann Nutr Metab. 1999;43:127–30. - PubMed
-
- Champagne CP, Fustier P. Microencapsulation for the improved delivery of bioactive compounds into foods. Curr Op Biotech. 2007;18:184–90. - PubMed
-
- Fahim TK, Zaidul ISM, Abu Bakar MR, Salim UM, Awang MB, Sahena F, Jalal KCA, Sharif KM, Sohrab MH. Particle formation and micronization using non-conventional techniques-review. Chem Eng Process: Process Intensification. 2014;86:47–52.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
