Phosphatidic Acid and Cardiolipin Coordinate Mitochondrial Dynamics
- PMID: 28911913
- PMCID: PMC5742555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.08.011
Phosphatidic Acid and Cardiolipin Coordinate Mitochondrial Dynamics
Abstract
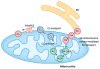
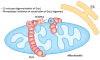
Membrane organelles comprise both proteins and lipids. Remodeling of these membrane structures is controlled by interactions between specific proteins and lipids. Mitochondrial structure and function depend on regulated fusion and the division of both the outer and inner membranes. Here we discuss recent advances in the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics by two critical phospholipids, phosphatidic acid (PA) and cardiolipin (CL). These two lipids interact with the core components of mitochondrial fusion and division (Opa1, mitofusin, and Drp1) to activate and inhibit these dynamin-related GTPases. Moreover, lipid-modifying enzymes such as phospholipases and lipid phosphatases may organize local lipid composition to spatially and temporarily coordinate a balance between fusion and division to establish mitochondrial morphology.
Keywords: dynamin-related GTPase; lipid phosphatase; membrane; mitochondrial division; mitochondrial fusion; phospholipase; phospholipids.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gustafsson CM, et al. Maintenance and Expression of Mammalian Mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 2016;85:133–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

