ROS induced distribution of mitochondria to filopodia by Myo19 depends on a class specific tryptophan in the motor domain
- PMID: 28912530
- PMCID: PMC5599611
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11002-9
ROS induced distribution of mitochondria to filopodia by Myo19 depends on a class specific tryptophan in the motor domain
Abstract
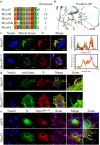
The role of the actin cytoskeleton in relation to mitochondria function and dynamics is only recently beginning to be recognized. Myo19 is an actin-based motor that is bound to the outer mitochondrial membrane and promotes the localization of mitochondria to filopodia in response to glucose starvation. However, how glucose starvation induces mitochondria localization to filopodia, what are the dynamics of this process and which enzymatic adaptation allows the translocation of mitochondria to filopodia are not known. Here we show that reactive oxygen species (ROS) mimic and mediate the glucose starvation induced phenotype. In addition, time-lapse fluorescent microscopy reveals that ROS-induced Myo19 motility is a highly dynamic process which is coupled to filopodia elongation and retraction. Interestingly, Myo19 motility is inhibited by back-to-consensus-mutation of a unique residue of class XIX myosins in the motor domain. Kinetic analysis of the purified mutant Myo19 motor domain reveals that the duty ratio (time spent strongly bound to actin) is highly compromised in comparison to that of the WT motor domain, indicating that Myo19 unique motor properties are necessary to propel mitochondria to filopodia tips. In summary, our study demonstrates the contribution of actin-based motility to the mitochondrial localization to filopodia by specific cellular cues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




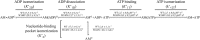



Similar articles
-
Kinetic adaptation of human Myo19 for active mitochondrial transport to growing filopodia tips.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 14;7(1):11596. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11984-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28912602 Free PMC article.
-
Myo19 is an outer mitochondrial membrane motor and effector of starvation-induced filopodia.J Cell Sci. 2016 Feb 1;129(3):543-56. doi: 10.1242/jcs.175349. Epub 2015 Dec 11. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 26659663
-
Biochemical and bioinformatic analysis of the myosin-XIX motor domain.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013 May;70(5):281-95. doi: 10.1002/cm.21110. Epub 2013 May 2. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013. PMID: 23568824 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin XIX.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1239:439-451. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38062-5_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32451871 Review.
-
Myosin-X: a MyTH-FERM myosin at the tips of filopodia.J Cell Sci. 2011 Nov 15;124(Pt 22):3733-41. doi: 10.1242/jcs.023549. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 22124140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fatal dysfunction and disintegration of thrombin-stimulated platelets.Haematologica. 2019 Sep;104(9):1866-1878. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.202309. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 30792211 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple links between actin and mitochondria.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Sep;24(9):651-667. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00613-y. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37277471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered mitochondrial trafficking as a novel mechanism of cancer metastasis.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2020 Feb;3(1):e1157. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1157. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 32671955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MyMOMA domain of MYO19 encodes for distinct Miro-dependent and Miro-independent mechanisms of interaction with mitochondrial membranes.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020 Mar;77(3-4):149-166. doi: 10.1002/cm.21560. Epub 2019 Sep 14. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 31479585 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramide-mediated orchestration of oxidative stress response through filopodia-derived small extracellular vesicles.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Jul;13(7):e12477. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12477. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 38988257 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

