Blood purification treatment initiated at the time of sepsis diagnosis effectively attenuates serum HMGB1 upregulation and improves patient prognosis
- PMID: 28912856
- PMCID: PMC5585716
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4854
Blood purification treatment initiated at the time of sepsis diagnosis effectively attenuates serum HMGB1 upregulation and improves patient prognosis
Abstract
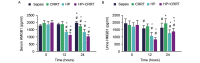
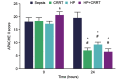
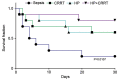
The aim of the present study was to investigate the increase in serum and urine levels of high mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) during sepsis and the effect of blood purification treatments on HMGB1 levels and patient prognosis. A total of 40 intensive care patients with sepsis were randomly assigned to different groups (n=10 per group): A control group (sepsis group), a continuous renal replacement treatment (CRRT) group, a hemoperfusion (HP) group and an HP+CRRT group. The blood purification treatments using HP and/or CRRT were performed immediately after the diagnosis of sepsis. HMGB1 levels were measured using ELISA, and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II scores and 30-day survival rates were evaluated. Relative to a healthy control group (n=10), HMGB1 levels were observed to be significantly upregulated during sepsis (P<0.05). Following the initiation of sepsis, serum HMGB1 continued to increase in the sepsis group and was significantly elevated at 24 h (P<0.05), whereas urine HMGB1 levels decreased significantly at 12 and 24 h (P<0.05). Serum HMGB1 levels were significantly positively correlated with APACHE II scores (r=0.7284, P<0.01) and significantly negatively correlated with urine HMGB1 levels (r=-0.5103, P=0.026). Serum HMGB1 levels were significantly reduced in the HP and HP+CRRT groups by 12 and 24 h following the initiation of treatment (both P<0.05). Changes in the urine HMGB1 level differed in each group. Relative to the sepsis group, the APACHE II scores of all blood purification groups were significantly reduced (P<0.05) and the 30-day survival rate of the HP+CRRT group was significantly increased (P=0.0107). The results of the present study indicate that blood purification initiated at the point of diagnosis in patients with sepsis may attenuate serum HMGB1 upregulation, promote urinary excretion of HMGB1 and improve the prognosis of sepsis.
Keywords: blood purification; excretion; high mobility group box protein 1; prognosis; sepsis.
Figures
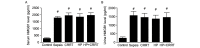
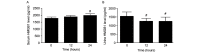
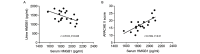
Similar articles
-
Mortality at 180-days is affected by serum haptoglobin levels in septic patients with high magnitude serum high mobility group box-1 levels.Acute Med Surg. 2022 Feb 1;9(1):e726. doi: 10.1002/ams2.726. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Acute Med Surg. 2022. PMID: 35127103 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of serum H-FABP, sTREM-1, and HMGB1 levels with severity and prognosis of sepsis.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):5846-5855. doi: 10.62347/KELZ4296. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39544769 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical study on application of intermittent hemofiltration combined with hemoperfusion in the early stage of severe burn in the prevention and treatment of sepsis].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2015 Aug;31(4):248-53. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26715634 Chinese.
-
[Effect of continuous blood purification and thymosin alpha1 on the cellular immunity in patients with severe sepsis: a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2009 Mar;21(3):139-42. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2009. PMID: 19278581 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Urine output is associated with prognosis in patients with acute kidney injury requiring continuous renal replacement therapy.J Crit Care. 2013 Aug;28(4):379-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.11.019. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 23582311
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Effect of Continuous Blood Purification Combined with Humanized Nursing in Patients with Severe Sepsis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 16;2022:1411371. doi: 10.1155/2022/1411371. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9863156. doi: 10.1155/2023/9863156. PMID: 36016678 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Biliary HMGB1 levels and biochemical indices in the assessment of acute obstructive septic cholangitis combined with septic shock.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025 Mar 6;80:100611. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100611. eCollection 2025. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025. PMID: 40054422 Free PMC article.
-
[Protective effect of early intervention with lipoxin A4 on septic mice].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jun;21(6):601-606. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2019.06.019. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31208517 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
microRNA-193-3p attenuates myocardial injury of mice with sepsis via STAT3/HMGB1 axis.J Transl Med. 2021 Sep 9;19(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03022-x. J Transl Med. 2021. Retraction in: J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 31;22(1):987. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05807-2. PMID: 34503521 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Association between thrombomodulin and high mobility group box 1 in sepsis patients.World J Crit Care Med. 2020 Oct 18;9(4):63-73. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v9.i4.63. eCollection 2020 Oct 18. World J Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 33134112 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
