Relationship Between Serum Total Testosterone Concentration and Augmentation Index at Radial Artery in Japanese Postmenopausal Patients
- PMID: 28912924
- PMCID: PMC5593435
- DOI: 10.14740/jocmr3164w
Relationship Between Serum Total Testosterone Concentration and Augmentation Index at Radial Artery in Japanese Postmenopausal Patients
Abstract
Background: The significance of testosterone as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) in females is controversial. This cross-sectional study aimed to elucidate the relationship between serum total testosterone concentration (T-T) and augmentation index at the radial artery (r-AIx) as a marker of arterial function in Japanese postmenopausal patients.
Methods: A total of 447 postmenopausal patients with traditional cardiovascular risk factors and/or a history of CVD (age (mean ± standard deviation (SD)), 73 ± 10 years) were enrolled. r-AIx was measured using tonometry, and the association between r-AIx and various clinical parameters, including T-T, was determined.
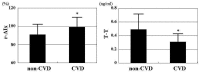
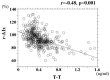
Results: r-AIx significantly increased (CVD vs. non-CVD: 99±11% vs. 91±11%, P < 0.001) and T-T significantly decreased (CVD vs. non-CVD: 0.31 ± 0.13 ng/mL vs. 0.49 ± 0.23 ng/mL, P < 0.001) in patients with CVD than in those without CVD. A significant negative correlation (r = -0.48; P < 0.001) between r-AIx and T-T was observed. Furthermore, multiple regression analysis indicated that T-T (t value = -7.7; P < 0.001), height (t value = -5.3; P < 0.001), d-ROMs test as a marker of oxidative stress in vivo (t value = 3.2; P < 0.001), CVD (t value = 2.9; P < 0.01), and pulse rate (t value = -2.7; P < 0.01) were independent variables for r-AIx as a subordinate factor.
Conclusion: This study revealed that low T-T is an important determining factor for an increase in r-AIx in Japanese postmenopausal patients. A prospective multicenter study with a large sample size is required to confirm the results of this study.
Keywords: Augmentation index; Cardiovascular disease; Female; Oxidative stress; Testosterone.
Conflict of interest statement
Author has no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Impact of Blood Testosterone Concentration on Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index in Female Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Cardiol Res. 2019 Feb;10(1):9-17. doi: 10.14740/cr827. Epub 2019 Feb 24. Cardiol Res. 2019. PMID: 30834054 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of the augmentation index in patients with preserved kidney function.J Nippon Med Sch. 2012;79(6):422-9. doi: 10.1272/jnms.79.422. J Nippon Med Sch. 2012. PMID: 23291840
-
Association between arterial stiffness and peripheral artery disease as measured by radial artery tonometry.J Vasc Surg. 2017 Nov;66(5):1518-1526. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.06.068. Epub 2017 Jul 26. J Vasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 28756044 Free PMC article.
-
High aortic augmentation index predicts mortality and cardiovascular events in men from a general population, but not in women.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2013 Dec;20(6):1005-12. doi: 10.1177/2047487312449588. Epub 2012 May 30. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 22649125
-
Skin autofluorescence, arterial stiffness and Framingham risk score as predictors of clinical outcome in chronic kidney disease patients: a cohort study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019 Mar 1;34(3):442-448. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx371. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019. PMID: 29378035
Cited by
-
Clinical Impact of Blood Testosterone Concentration on Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index in Female Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Cardiol Res. 2019 Feb;10(1):9-17. doi: 10.14740/cr827. Epub 2019 Feb 24. Cardiol Res. 2019. PMID: 30834054 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Serum Total Testosterone Concentration in Japanese Elderly Women With Pre-Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.Cardiol Res. 2025 Jun 9;16(4):346-352. doi: 10.14740/cr2084. eCollection 2025 Aug. Cardiol Res. 2025. PMID: 40809732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ziemens B, Wallaschofski H, Volzke H, Rettig R, Dorr M, Nauck M, Keevil BG. et al. Positive association between testosterone, blood pressure, and hypertension in women: longitudinal findings from the Study of Health in Pomerania. J Hypertens. 2013;31(6):1106–1113. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283603eb1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patel SM, Ratcliffe SJ, Reilly MP, Weinstein R, Bhasin S, Blackman MR, Cauley JA. et al. Higher serum testosterone concentration in older women is associated with insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94(12):4776–4784. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-0740. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sievers C, Klotsche J, Pieper L, Schneider HJ, Marz W, Wittchen HU, Stalla GK. et al. Low testosterone levels predict all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in women: a prospective cohort study in German primary care patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2010;163(4):699–708. doi: 10.1530/EJE-10-0307. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
