Baicalin Attenuates Subarachnoid Hemorrhagic Brain Injury by Modulating Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption, Inflammation, and Oxidative Damage in Mice
- PMID: 28912935
- PMCID: PMC5587966
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/1401790
Baicalin Attenuates Subarachnoid Hemorrhagic Brain Injury by Modulating Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption, Inflammation, and Oxidative Damage in Mice
Abstract
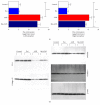
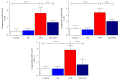
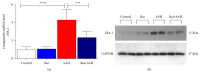
In subarachnoid hemorrhagic brain injury, the early crucial events are edema formation due to inflammatory responses and blood-brain barrier disruption. Baicalin, a flavone glycoside, has antineuroinflammatory and antioxidant properties. We examined the effect of baicalin in subarachnoid hemorrhagic brain injury. Subarachnoid hemorrhage was induced through filament perforation and either baicalin or vehicle was administered 30 min prior to surgery. Brain tissues were collected 24 hours after surgery after evaluation of neurological scores. Brain tissues were processed for water content, real-time PCR, and immunoblot analyses. Baicalin improved neurological score and brain water content. Decreased levels of tight junction proteins (occludin, claudin-5, ZO-1, and collagen IV) required for blood-brain barrier function were restored to normal level by baicalin. Real-time PCR data demonstrated that baicalin attenuated increased proinflammatory cytokine (IL-1β, IL-6, and CXCL-3) production in subarachnoid hemorrhage mice. In addition to that, baicalin attenuated microglial cell secretion of IL-1β and IL-6 induced by lipopolysaccharide (100 ng/ml) dose dependently. Finally, baicalin attenuated induction of NOS-2 and NOX-2 in SAH mice at the mRNA and protein level. Thus, we demonstrated that baicalin inhibited microglial cell activation and reduced inflammation, oxidative damage, and brain edema.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
Melatonin attenuates inflammatory response-induced brain edema in early brain injury following a subarachnoid hemorrhage: a possible role for the regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines.J Pineal Res. 2014 Oct;57(3):340-7. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12173. Epub 2014 Sep 15. J Pineal Res. 2014. PMID: 25187344
-
Minocycline Protects Against NLRP3 Inflammasome-Induced Inflammation and P53-Associated Apoptosis in Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 May;53(4):2668-78. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9318-8. Epub 2015 Jul 5. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26143258
-
Underlying Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Molecular Targets in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(12):1168-1179. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200106154203. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31903882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting TLR4-dependent inflammation in post-hemorrhagic brain injury.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Jun;24(6):525-533. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1752182. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 32249624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation of baicalin-loaded ligand-modified nanoparticles for nose-to-brain delivery for neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):1282-1298. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2064564. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35467483 Free PMC article.
-
Phytotherapy and the Role of Bioactive Compounds in Modulating Mechanisms of Overweight and Obesity Comorbid with Depressive Symptoms-A Scoping Review of Mechanisms of Action.Molecules. 2025 Jun 30;30(13):2827. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132827. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649341 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of flavonoids against intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2024 Jul 4;28(3):350. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12639. eCollection 2024 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39071910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalin Prevents Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibiting ACSL4 Mediated Ferroptosis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 14;12:628988. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.628988. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33935719 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalin plays a protective role by regulating ferroptosis in multiple diseases.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May;398(5):4837-4849. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03704-5. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39661143 Review.
References
-
- Haley E. C., Jr., Kassell N. F., Torner J. C. The International Cooperative Study on the timing of aneurysm surgery. The North American experience. Stroke. 1992;23:205–214. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

