Sporotrichoid-Like Spread of Cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae in an Immunocompromised Patient
- PMID: 28912980
- PMCID: PMC5587931
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8219841
Sporotrichoid-Like Spread of Cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae in an Immunocompromised Patient
Abstract
Mycobacterium chelonae is a rapidly growing mycobacterium found in water and soil that can cause local cutaneous infections in immunocompetent hosts but more frequently affects immunocompromised patients. Typically, patients will present with painful subcutaneous nodules of the joints or soft tissues from traumatic inoculation. However, exhibiting a sporotrichoid-like pattern of these nodules is uncommon. Herein, we report a case of sporotrichoid-like distribution of cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus on significant immunosuppressive medications. Clinicians treating immunocompromised patients should be cognizant of their propensity to develop unusual infections and atypical presentations.
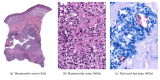
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recurrence of cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae infection: A case report.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019 Apr 26;7:2050313X19845231. doi: 10.1177/2050313X19845231. eCollection 2019. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31065356 Free PMC article.
-
A case of cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae abscessus infection in a renal transplant patient.J Cutan Med Surg. 2001 Jan-Feb;5(1):28-32. doi: 10.1177/120347540100500107. J Cutan Med Surg. 2001. PMID: 11281431
-
Disseminated cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae infection with multidrug resistance in a patient with panuveitis.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008 May;33(3):256-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2007.02605.x. Epub 2007 Nov 15. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18021269
-
Mycobacterium marinum infections in transplant recipients: case report and review of the literature.Transpl Infect Dis. 2008 Oct;10(5):358-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3062.2008.00317.x. Epub 2008 May 15. Transpl Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18482202 Review.
-
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria: Skin and Soft Tissue Infections.Dermatol Clin. 2015 Jul;33(3):563-77. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2015.03.017. Epub 2015 May 8. Dermatol Clin. 2015. PMID: 26143432 Review.
Cited by
-
Recurrent Mycobacterium chelonae Skin Infection Unmasked as Factitious Disorder Using Bacterial Whole Genome Sequence Analysis.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 22;7(11):ofaa506. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa506. eCollection 2020 Nov. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33204765 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrence of cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae infection: A case report.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019 Apr 26;7:2050313X19845231. doi: 10.1177/2050313X19845231. eCollection 2019. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31065356 Free PMC article.
-
Disseminated Cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae Infection in an Immunocompetent Patient.Cureus. 2023 Aug 8;15(8):e43170. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43170. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37692700 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of Osteomyelitis of an Ankle Caused by Mycobacterium chelonae.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;12(1):97. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010097. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higgins E. M., Lawrence C. M. Sporotrichoid spread of Mycobacterium chelonei. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 1988;13:234–236. - PubMed
-
- Wallace R. J., Brown B. A., Onyi G. O. Skin, soft tissue, and bone infections due to Mycobacterium chelonae chelonae: importance of prior corticosteroid therapy, frequency of disseminated infections, and resistance to oral antimicrobials other than clarithromycin. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1992;166(2):405–412. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.405. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schwendiman M. N., Johnson R. P., Henning J. S. Subcutaneous nodules with sporotrichoid spread. Dermatology Online JournaL. 2009;15(5):p. 11. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources