The Efficacy of Coblator in Turbinoplasty
- PMID: 28913312
- PMCID: PMC5556901
- DOI: 10.7181/acfs.2017.18.2.82
The Efficacy of Coblator in Turbinoplasty
Abstract
Background: Turbinate hypertrophy is one of the common causes of chronic nasal obstruction. In principle, therapeutic guidelines recommend medical treatment. Failure to treat turbinate thickening despite drug therapy may indicate the need for surgery. The main aim of this study was to determine the effect of radiofrequency surgery, among various other surgical procedures, on people with both nasal septal deviation and turbinate hypertrophy.
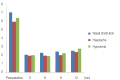
Methods: Among people with nasal deviation who visited the subject hospital between July 2008 to July 2014, 21 people with nasal septal deviation and severe turbinate hypertrophy before their surgery had undergone septoplasty with turbinoplasty using radiofrequency combined with septoplasty. The degree of the turbinate's hypertrophy was appraised in all the patients before and after the surgery using the rhinoscopy, and acoustic rhinometry was objectively carried out. The subjective effect of the turbinoplasty using radiofrequency was explored through the visual analog scale (VAS) score.
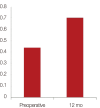
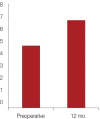
Results: The degree of contraction of the nasal mucosa after the rhinoscopy changed from Grades 3 and 4 (100%) to Grades 1 and 2 (95.2%) and Grades 3 (4.8%). The minimal cross-sectional area significantly increased from 0.44±0.07 to 0.70±0.07 cm2 (p<0.05). The nasal cavity volume increased from 4.79±0.49 to 6.76±0.55 cm2 (p<0.05). The subjective symptoms evaluated with VAS score a year after the surgery significantly improved (p<0.05).
Conclusion: Turbinoplasty using Coblator with septoplasty is an effective treatment method because it expands nasal cavity, has a low incidence of complications, subjectively improves symptoms, and has short treatment duration.
Keywords: Nasal cavity; Nasal obstruction; Rhinoplasty; Turbinates.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Lavinsky-Wolff M, Camargo HL, Jr, Barone CR, Rabaioli L, Wolff FH, Dolci JE, et al. Effect of turbinate surgery in rhinoseptoplasty on quality-of-life and acoustic rhinometry outcomes: a randomized clinical trial. Laryngoscope. 2013;123:82–89. - PubMed
-
- Berger G, Hammel I, Berger R, Avraham S, Ophir D. Histopathology of the inferior turbinate with compensatory hypertrophy in patients with deviated nasal septum. Laryngoscope. 2000;110:2100–2105. - PubMed
-
- Liu CM, Tan CD, Lee FP, Lin KN, Huang HM. Microdebrider-assisted versus radiofrequency-assisted inferior turbinoplasty. Laryngoscope. 2009;119:414–418. - PubMed
-
- Lee KC, Hwang PH, Kingdom TT. Surgical management of inferior turbinate hypertrophy in the office: Three mucosal sparing techniques. Oper Tech Otolayngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;12:107–111.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

