Validation of the American Joint Commission on Cancer (8th edition) changes for patients with stage III gastric cancer: survival analysis of a large series from a Specialized Eastern Center
- PMID: 28913982
- PMCID: PMC5633559
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1118
Validation of the American Joint Commission on Cancer (8th edition) changes for patients with stage III gastric cancer: survival analysis of a large series from a Specialized Eastern Center
Abstract
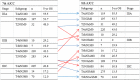
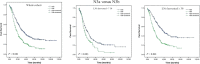
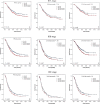
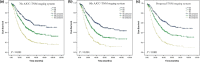
The 8th edition of the TNM was released in 2016 and included major revisions, especially for stage III. We aimed to compare the prognostic value of the 7th and 8th editions of the AJCC TNM classification for stage III gastric cancer. Clinical data from 1557 patients operated on for stage III gastric cancer according to the 7th edition between 2007 and 2014 were analyzed and compared using the 7th and 8th TNM classifications. A proposed staging system was established, and the three systems were compared in terms of prognostic performance. The stage shifted for 669 (42.96%) patients. It shifted from IIIA to IIIB (one patient, 0.06%), IIIB to IIIA (230 patients, 14.8%), IIIB to IIIC (94 patients, 6.0%), and IIIC to IIIB (344 patients, 22.1%). However, the new AJCC subgroupings did not prove distinctive for survival levels between T3N3aM0 (stage IIIB) and T3N3bM0 (stage IIIC) or between T4aN3aM0 (stage IIIB) and T4aN3bM0 (stage IIIC) when <30 lymph nodes (LNs) were resected. The performance of the 8th edition (c-index, 0.614; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.596-0.633) revealed no relevant improvement compared to the 7th edition (c-index, 0.624; 95% CI, 0.605-0.643). The proposed staging system generated the best prognostic stratification. The 8th TNM edition may not provide better accuracy in predicting the prognosis of stage III gastric cancer. The proposed staging system, comprised of a combination of the number of LNs harvested and the 7th and 8th AJCC classifications, may improve predictive capacities for stage III gastric cancer.
Keywords: TNM stage; gastric cancer; surgical oncology; survival.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Ajani, J. A. , In H., Sano T., et al. 2016. Stomach Pp. 203‐220, in Amin M. B., ed. AJCC cancer staging manual, 8th ed Springer, New York.
-
- Edge, S. B. , Byrd D. R., Compton C. C., et al. 2010. AJCC cancer staging handbook, 7th ed. Springer, New York, NY.
-
- Röcken, C. , and Behrens H. M., 2015. Validating the prognostic and discriminating value of the TNM‐classification for gastric cancer – a critical appraisal. Eur. J. Cancer 51:577–586. - PubMed
-
- Wang, J. , Dang P., Raut C. P., Pandalai P. K., Maduekwe U. N., Rattner D. W., et al. 2012. Comparison of a lymph node ratio‐based staging system with the 7th AJCC system for gastric cancer: analysis of 18,043 patients from the SEER database. Ann. Surg. 255:478–485. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

