IF2 and unique features of initiator tRNAfMet help establish the translational reading frame
- PMID: 28914580
- PMCID: PMC6103701
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1379636
IF2 and unique features of initiator tRNAfMet help establish the translational reading frame
Abstract
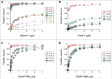
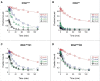
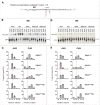
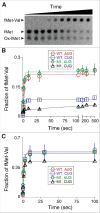
Translation begins at AUG, GUG, or UUG codons in bacteria. Start codon recognition occurs in the P site, which may help explain this first-position degeneracy. However, the molecular basis of start codon specificity remains unclear. In this study, we measured the codon dependence of 30S•mRNA•tRNAfMet and 30S•mRNA•tRNAMet complex formation. We found that complex stability varies over a large range with initiator tRNAfMet, following the same trend as reported previously for initiation rate in vivo (AUG > GUG, UUG > CUG, AUC, AUA > ACG). With elongator tRNAMet, the codon dependence of binding differs qualitatively, with virtually no discrimination between GUG and CUG. A unique feature of initiator tRNAfMet is a series of three G-C basepairs in the anticodon stem, which are known to be important for efficient initiation in vivo. A mutation targeting the central of these G-C basepairs causes the mRNA binding specificity pattern to change in a way reminiscent of elongator tRNAMet. Unexpectedly, for certain complexes containing fMet-tRNAfMet, we observed mispositioning of mRNA, such that codon 2 is no longer programmed in the A site. This mRNA mispositioning is exacerbated by the anticodon stem mutation and suppressed by IF2. These findings suggest that both IF2 and the unique anticodon stem of fMet-tRNAfMet help constrain mRNA positioning to set the correct reading frame during initiation.
Keywords: IF1; IF3; P site; initiation; ribosome; start codon selection.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural analysis of noncanonical translation initiation complexes.J Biol Chem. 2024 Oct;300(10):107743. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107743. Epub 2024 Sep 1. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39222680 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive contributions of the ribosomal P-site elements m2G966, m5C967 and the C-terminal tail of the S9 protein in the fidelity of initiation of translation in Escherichia coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 May;41(9):4963-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt175. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23530111 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the 30S translation initiation complex.Nature. 2008 Sep 18;455(7211):416-20. doi: 10.1038/nature07192. Epub 2008 Aug 31. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18758445
-
A structural view of translation initiation in bacteria.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Feb;66(3):423-36. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8416-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19011758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Initiation of mRNA translation in bacteria: structural and dynamic aspects.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Nov;72(22):4341-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2010-3. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26259514 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tuning tRNAs for improved translation.Front Genet. 2024 Jun 25;15:1436860. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1436860. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38983271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of sequestration of the anti-Shine-Dalgarno sequence in the Bacteroidetes ribosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 11;49(1):547-567. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1195. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33330920 Free PMC article.
-
Cys-tRNAj as a Second Translation Initiator for Priming Proteins with Cysteine in Bacteria.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 29;10(5):4548-4560. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08326. eCollection 2025 Feb 11. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39959092 Free PMC article.
-
Drop-off-reinitiation at the amino termini of nascent peptides and its regulation by IF3, EF-G, and RRF.RNA. 2023 May;29(5):663-674. doi: 10.1261/rna.079447.122. Epub 2023 Feb 8. RNA. 2023. PMID: 36754577 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomes lacking bS21 gain function to regulate protein synthesis in Flavobacterium johnsoniae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Feb 28;51(4):1927-1942. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad047. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36727479 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
