The association of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 28914694
- PMCID: PMC5675792
- DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000973
The association of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Background and aim: The association between obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and abnormal liver enzymes has been reported in multiple studies. The existing literature regarding the relationship between OSA and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is conflicting. Thus we aimed to determine the relationship between OSA and NASH from a large database.
Patients and methods: A cross-sectional study was performed using the 2012 Nationwide Inpatient Sample. We identified adult patients (18-90 years) who had a diagnosis of OSA using the International Classification of Diseases 9th version codes. The control group was comprised of adult individuals with no discharge records of OSA. NASH diagnosis was also identified using the International Classification of Diseases 9th version codes. The association between OSA and NASH was calculated using univariable and multivariable logistic regression.
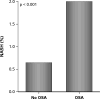
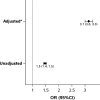
Results: A total of 30 712 524 hospitalizations were included. The OSA group included 1 490 150 patients versus 29 222 374 in the control non-OSA group. The OSA group average age was 61.8±0.07 years (44.2% females) compared with 57.0±0.11 years (60.1% females) in the non-OSA group. NASH prevalence was significantly higher in the OSA group compared with the non-OSA group [2% (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.9, 2.1) vs. 0.65% (95% CI: 0.63, 0.66), P<0.001]. After adjusting for obesity, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, the metabolic syndrome and Charlson comorbidity index, OSA patients were three times more likely to have NASH [adjusted odds ratio: 3.1 (95% CI: 3.0-3.3), P<0.001].
Conclusion: Patients with OSA are three times more likely to have NASH compared with patients without OSA after controlling for other confounders. These data indicate that OSA should be considered as an independent risk factor for developing NASH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Xu J, Tejada-Vera B. Deaths: Final Data for 2014. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2016;65(4):1–122. - PubMed
-
- Clark JM, Brancati FL, Diehl AM. The prevalence and etiology of elevated aminotransferase levels in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98(5):960–967. - PubMed
-
- Browning JD, Szczepaniak LS, Dobbins R, et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: Impact of ethnicity. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1387–1395. - PubMed
-
- Ludwig J, Viggiano TR, McGill DB, Oh BJ. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55(7):434–438. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical