Structural Evidence for the Dopamine-First Mechanism of Norcoclaurine Synthase
- PMID: 28915025
- PMCID: PMC5637010
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00769
Structural Evidence for the Dopamine-First Mechanism of Norcoclaurine Synthase
Abstract
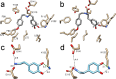
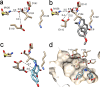
Norcoclaurine synthase (NCS) is a Pictet-Spenglerase that catalyzes the first key step in plant benzylisoquinoline alkaloid metabolism, a compound family that includes bioactive natural products such as morphine. The enzyme has also shown great potential as a biocatalyst for the formation of chiral isoquinolines. Here we present new high-resolution X-ray crystallography data describing Thalictrum flavum NCS bound to a mechanism-inspired ligand. The structure supports two key features of the NCS "dopamine-first" mechanism: the binding of dopamine catechol to Lys-122 and the position of the carbonyl substrate binding site at the active site entrance. The catalytically vital residue Glu-110 occupies a previously unobserved ligand-bound conformation that may be catalytically significant. The potential roles of inhibitory binding and alternative amino acid conformations in the mechanism have also been revealed. This work significantly advances our understanding of the NCS mechanism and will aid future efforts to engineer the substrate scope and catalytic properties of this useful biocatalyst.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural basis of enzymatic (S)-norcoclaurine biosynthesis.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 9;284(2):897-904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803738200. Epub 2008 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19004827
-
'Dopamine-first' mechanism enables the rational engineering of the norcoclaurine synthase aldehyde activity profile.FEBS J. 2015 Mar;282(6):1137-51. doi: 10.1111/febs.13208. Epub 2015 Feb 9. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25620686 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of norcoclaurine synthase, an enzyme catalyzing the first committed step in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis.Plant J. 2004 Oct;40(2):302-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02210.x. Plant J. 2004. PMID: 15447655
-
Norcoclaurine synthase: mechanism of an enantioselective pictet-spengler catalyzing enzyme.Molecules. 2010 Mar 24;15(4):2070-8. doi: 10.3390/molecules15042070. Molecules. 2010. PMID: 20428026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Occurrence of Enantioselectivity in Nature: The Case of (S)-Norcoclaurine.Chirality. 2016 Mar;28(3):169-80. doi: 10.1002/chir.22566. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Chirality. 2016. PMID: 26729048 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a missing Pictet-Spenglerase in the Gloriosa superba L. colchicine biosynthesis pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 18;52(1):244. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10364-y. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39964647
-
Characterization of norbelladine synthase and noroxomaritidine/norcraugsodine reductase reveals a novel catalytic route for the biosynthesis of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids including the Alzheimer's drug galanthamine.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 30;14:1231809. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1231809. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37711303 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic Phosphate-Catalyzed Pictet-Spengler Reaction for the Synthesis of 1,1'-Disubstituted and Spiro-Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloids.J Org Chem. 2019 Jun 21;84(12):7702-7710. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.9b00527. Epub 2019 May 31. J Org Chem. 2019. PMID: 31095375 Free PMC article.
-
Rational Engineering of (S)-Norcoclaurine Synthase for Efficient Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids Biosynthesis.Molecules. 2023 May 23;28(11):4265. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114265. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37298742 Free PMC article.
-
Over 100 Million Years of Enzyme Evolution Underpinning the Production of Morphine in the Papaveraceae Family of Flowering Plants.Plant Commun. 2020 Mar 9;1(2):100029. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100029. Plant Commun. 2020. PMID: 32685922 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

