Protection by Inhaled Hydrogen Therapy in a Rat Model of Acute Lung Injury can be Tracked in vivo Using Molecular Imaging
- PMID: 28915216
- PMCID: PMC5636640
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000872
Protection by Inhaled Hydrogen Therapy in a Rat Model of Acute Lung Injury can be Tracked in vivo Using Molecular Imaging
Abstract
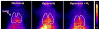
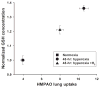
Inhaled hydrogen gas (H2) provides protection in rat models of human acute lung injury (ALI). We previously reported that biomarker imaging can detect oxidative stress and endothelial cell death in vivo in a rat model of ALI. Our objective was to evaluate the ability of Tc-hexamethylpropyleneamineoxime (HMPAO) and Tc-duramycin to track the effectiveness of H2 therapy in vivo in the hyperoxia rat model of ALI. Rats were exposed to room air (normoxia), 98% O2 + 2% N2 (hyperoxia) or 98% O2 + 2% H2 (hyperoxia+H2) for up to 60 h. In vivo scintigraphy images were acquired following injection of Tc-HMPAO or Tc-duramycin. For hyperoxia rats, Tc-HMPAO and Tc-duramycin lung uptake increased in a time-dependent manner, reaching a maximum increase of 270% and 150% at 60 h, respectively. These increases were reduced to 120% and 70%, respectively, in hyperoxia+H2 rats. Hyperoxia exposure increased glutathione content in lung homogenate (36%) more than hyperoxia+H2 (21%), consistent with increases measured in Tc-HMPAO lung uptake. In 60-h hyperoxia rats, pleural effusion, which was undetectable in normoxia rats, averaged 9.3 gram/rat, and lung tissue 3-nitrotyrosine expression increased by 790%. Increases were reduced by 69% and 59%, respectively, in 60-h hyperoxia+H2 rats. This study detects and tracks the anti-oxidant and anti-apoptotic properties of H2 therapy in vivo after as early as 24 h of hyperoxia exposure. The results suggest the potential utility of these SPECT biomarkers for in vivo assessment of key cellular pathways in the pathogenesis of ALI and for monitoring responses to therapies.
Figures





References
-
- Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E, Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley DF, Ranieri M, Rubenfeld G, Thompson BT, Wrigge H, Slutsky AS, Pesenti A. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. Jama. 2016;315:788–800. - PubMed
-
- Girardis M, Busani S, Damiani E, Donati A, Rinaldi L, Marudi A, Morelli A, Antonelli M, Singer M. Effect of Conservative vs Conventional Oxygen Therapy on Mortality Among Patients in an Intensive Care Unit: The Oxygen-ICU Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama. 2016;316:1583–1589. - PubMed
-
- Crapo JD, Barry BE, Foscue HA, Shelburne J. Structural and biochemical changes in rat lungs occurring during exposures to lethal and adaptive doses of oxygen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980;122:123–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

