Albuminuria and Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 28915230
- PMCID: PMC5612264
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.903660
Albuminuria and Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
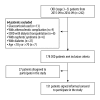
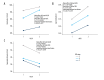
BACKGROUND Albuminuria has been associated with cardiovascular events, but whether such an association can be explained by endothelial dysfunction is not fully understood. In this study, we examined the relationship between the urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) and biomarkers of endothelial function in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). MATERIAL AND METHODS The cross-sectional associations of renal dysfunction and UACR with procoagulant and inflammatory factors were evaluated for 151 consecutive CKD (stage 3-5) patients. Subjects were grouped by UACR (≤300 mg/g or >300 mg/g) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (30≤ eGFR <60, 15≤ eGFR <30, or eGFR <15 ml/min per 1.73 m²). RESULTS A higher UACR level was associated with an increase in von Willebrand factor antigen (vWF: Ag) levels, vWF activity, factor VIII, interleukin-2, and log (interleukin-6), even after adjustment for risk factors. Linear regression analysis indicated that for every 88.5 mg/g increase in UACR, the vWF activity and factor VIII were elevated by 8.3% and 6.3%, respectively. The factorial design ANOVA data showed no statistically significant interaction between UACR and CKD stage with procoagulant and inflammatory factors. CONCLUSIONS Our study shows an eGFR-independent association of higher UACR with elevations in markers of endothelial dysfunction and inflammatory factors in CKD patients.
Figures

References
-
- Tonelli M, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani R. Epidemiology and mechanisms of uremia-related cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2016;133:518–36. - PubMed
-
- Schiffrin EL, Lipman ML, Mann JF. Chronic kidney disease: effects on the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 2007;116:85–97. - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–305. - PubMed
-
- Hogas SM, Voroneanu L, Serban DN, et al. Methods and potential biomarkers for the evaluation of endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease: A critical approach. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2010;4:116–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

