Associations between body mass index and mortality or cardiovascular events in a general Korean population
- PMID: 28915262
- PMCID: PMC5600387
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185024
Associations between body mass index and mortality or cardiovascular events in a general Korean population
Abstract
Background/objectives: The relationship between body mass index (BMI) and mortality remains controversial. Furthermore, the association between BMI and cardiovascular events (CVE) is not conclusive and may differ by ethnicity. We aimed to estimate the associations between the BMI and mortality or cardiovascular disease in a general Korean population.
Subjects/methods: This study was based on a sample cohort database released by the Korean National Health Insurance Service. We analyzed a total of 415,796 adults older than 30 years of age who had undergone a national health examination at least once from 2002 to 2012. Hazard ratios for death and cardiovascular events were calculated using Cox proportional hazards models.
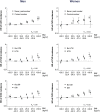
Results: For both men and women, BMI and overall mortality showed a U-shaped association, with the lowest mortality rate among those with a BMI of 25-27.4 kg/m2. Compared with them, subjects with a BMI ≥ 30kg/m2, men with a BMI < 25 kg/m2, and women with a BMI < 22.5 kg/m2 showed significantly higher overall mortality. Additionally, men with a BMI < 22.5 kg/m2 and women with a BMI < 20 kg/m2 displayed an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality. Unlike the mortality trend, the CVD events trend showed a linearly positive association. The risk of a CVE was the lowest in men with a BMI ranging from 20 to 22.4 kg/m2 and in women with a BMI < 20 kg/m2.
Conclusions: The BMI showed a U-shaped association with overall mortality, where slightly obese subjects showed the lowest rate of mortality. The CVE exhibited a linear association with the BMI, where the lowest risk was observed for normal weight subjects in a general Korean population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Sullivan L, Parise H, Kannel WB. Overweight and obesity as determinants of cardiovascular risk: the Framingham experience. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2002; 162: 1867–72. - PubMed
-
- Feigin VL, Rinkel GJ, Lawes CM, Algra A, Bennett DA, van Gijn J, et al. Risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage: an updated systematic review of epidemiological studies. Stroke. 2005; 36: 2773–80. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000190838.02954.e8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jee SH, Sull JW, Park J, Lee SY, Ohrr H, Guallar E, et al. Body-mass index and mortality in Korean men and women. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2006; 355: 779–87. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa054017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zheng W, McLerran DF, Rolland B, Zhang X, Inoue M, Matsuo K, et al. Association between body-mass index and risk of death in more than 1 million Asians. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2011; 364: 719–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1010679 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gu D, He J, Duan X, Reynolds K, Wu X, Chen J, et al. Body weight and mortality among men and women in China. JAMA. 2006; 295: 776–83. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.7.776 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

