Reevaluation of ATR signaling in primary resting chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: evidence for pro-survival or pro-apoptotic function
- PMID: 28915641
- PMCID: PMC5593612
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18144
Reevaluation of ATR signaling in primary resting chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: evidence for pro-survival or pro-apoptotic function
Abstract
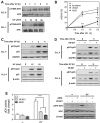
ATM, primarily activated by DNA double-strand breaks, and ATR, activated by single-stranded DNA, are master regulators of the cellular response to DNA damage. In primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells, ATR signaling is considered to be switched off due to ATR downregulation. Here, we hypothesized that ATR, though expressed at low protein level, could play a role in primary resting CLL cells after genotoxic stress. By investigating the response of CLL cells to UV-C irradiation, a prototypical activator of ATR, we could detect phosphorylation of ATR at Thr-1989, a marker for ATR activation, and also observed that selective ATR inhibitors markedly decreased UV-C-induced phosphorylation of ATR targets, including H2AX and p53. Similar results were obtained with the purine analogs fludarabine and cladribine that were also shown to activate ATR and induce ATR-dependent phosphorylation of H2AX and p53. In addition, ATR inhibition was found to sensitize primary CLL cells to UV-C by decreasing DNA repair synthesis. Conversely, ATR inhibition rescued CLL cells against purine analogs by reducing expression of the pro-apoptotic genes PUMA and BAX. Collectively, our study indicates that ATR signaling can be activated in resting CLL cells and play a pro-survival or pro-apoptotic role, depending on the genotoxic context.
Keywords: ATR; CLL; UV-C; fludarabine; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:804–815. - PubMed
-
- Cramer P, Hallek M. Prognostic factors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia-what do we need to know? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8:38–47. - PubMed
-
- Dohner H, Fischer K, Bentz M, Hansen K, Benner A, Cabot G, Diehl D, Schlenk R, Coy J, Stilgenbauer S, Volkmann M, Galle PR, Poustka A, et al. p53 gene deletion predicts for poor survival and non-response to therapy with purine analogs in chronic B-cell leukemias. Blood. 1995;85:1580–1589. - PubMed
-
- Zenz T, Eichhorst B, Busch R, Denzel T, Habe S, Winkler D, Buhler A, Edelmann J, Bergmann M, Hopfinger G, Hensel M, Hallek M, Dohner H, et al. TP53 mutation and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4473–4479. - PubMed
-
- Roos WP, Kaina B. DNA damage-induced cell death: from specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2013;332:237–248. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

