Biomarker analysis of the phase 3 TORCH trial for first line erlotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients
- PMID: 28915692
- PMCID: PMC5593664
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15725
Biomarker analysis of the phase 3 TORCH trial for first line erlotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients
Abstract
Background: The TORCH phase III trial compared the efficacy of first-line erlotinib followed by chemotherapy at progression (experimental arm) with the reverse sequence (standard arm) in unselected advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Here we report biomarker analyses.
Methods: EGFR and KRAS mutation, expression of EGFR family members and of cMET and PTEN and EGFR and ABCG2 germline polymorphisms were tested on tumor tissue or blood samples to either confirm previously proposed predictive role or describe it in an explorative setting. Progression-free survival (PFS) was the primary end-point, overall survival, response rate and side effects (diarrhoea and skin toxicity) were secondary end-points. Interactions between biomarkers and treatment were studied with multivariable models (either Cox model or logistic regression). Statistical analyses accounted for multiple comparisons.
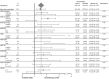
Results: At least one biomarker was assessed in 324 out of 760 patients in the TORCH study. EGFR mutation was more common in female (P = 0.0001), East Asians (P < 0.0001) and never smoker (P < 0.0001) patients; low MET protein expression by IHC (H-score <200) was more frequent in squamous (P < 0.00009) and ABCG2 C/A or A/A polymorphism was more frequent among East-Asian patients (P = 0.0003). A significant interaction was found for EGFR mutation in PFS and response rate analyses while no predictive effect on OS was found for any biomarker. No biomarker tested was prognostic for PFS and OS. No polymorphism was significantly associated with skin toxicity or diarrhea.
Conclusion: In the present study, beyond the known role of EGFR mutation, no other biomarker has predictive or prognostic role.
Keywords: EGFR TKI; NSCLC; biomarker analysis; predictive factors; prognostic factors.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST M.Tsao and F.Perrone have received research funding from Roche. G.Liu, C.Butts, F.Ciardiello, A.Morabito, F.Perrone and C.Gridelli have received honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boeringher Ingelheim and Roche. A. Rossi has received honoraria from AstraZeneca and Boeringher Ingelheim.
Figures


References
-
- Besse B, Adjei A, Baas P, Meldgaard P, Nicolson M, Paz-Ares L, Reck M, Smit EF, Syrigos K, Stahel R, Felip E, Peters S, Panel M, et al. 2nd ESMO Consensus Conference on Lung Cancer: non-small-cell lung cancer first-line/second and further lines of treatment in advanced disease. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:1475–84. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu123. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, Asami K, Katakami N, Takada M, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–8. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70364-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–46. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70393-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, Lu S, Zhang L, Hu C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70184-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

