Antibiotic resistance: it's bad, but why isn't it worse?
- PMID: 28915805
- PMCID: PMC5603022
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-017-0423-1
Antibiotic resistance: it's bad, but why isn't it worse?
Abstract
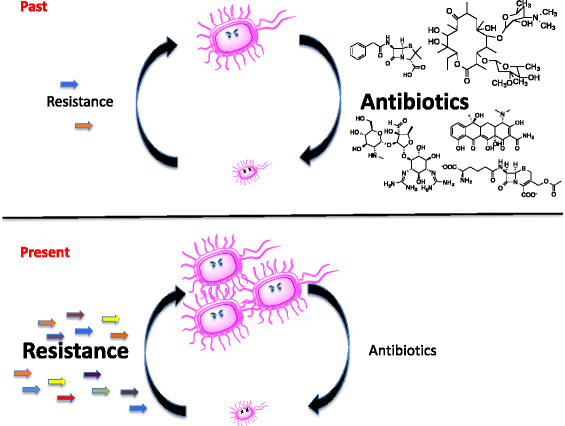
Antibiotic natural products are ancient and so is resistance. Consequently, environmental bacteria harbor numerous and varied antibiotic resistance elements. Nevertheless, despite long histories of antibiotic production and exposure, environmental bacteria are not resistant to all known antibiotics. This means that there are barriers to the acquisition of a complete resistance armamentarium. The sources, distribution, and movement of resistance mechanisms in different microbes and bacterial populations are mosaic features that act as barriers to slow this movement, thus moderating the emergence of bacterial pan-resistance. This is highly relevant to understanding the emergence of resistance in pathogenic bacteria that can inform better antibiotic management practices and influence new drug discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lessons from the Environmental Antibiotic Resistome.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;71:309-329. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-090816-093420. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28657887 Review.
-
Antibiotic resistance in the environment: a link to the clinic?Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Oct;13(5):589-94. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.08.005. Epub 2010 Sep 16. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20850375 Review.
-
General principles of antibiotic resistance in bacteria.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2014 Mar;11:33-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2014.02.001. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2014. PMID: 24847651 Review.
-
Environmental pollution by antibiotics and by antibiotic resistance determinants.Environ Pollut. 2009 Nov;157(11):2893-902. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.05.051. Epub 2009 Jun 27. Environ Pollut. 2009. PMID: 19560847 Review.
-
Identification of antibiotic resistant bacteria community and a GeoChip based study of resistome in urban watersheds.Water Res. 2016 Dec 1;106:330-338. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.032. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Water Res. 2016. PMID: 27750121
Cited by
-
Vancomycin Resistance in Enterococcus and Staphylococcus aureus.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 21;11(1):24. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010024. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin E Increases Antimicrobial Sensitivity by Inhibiting Bacterial Lipocalin Antibiotic Binding.mSphere. 2018 Dec 12;3(6):e00564-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00564-18. mSphere. 2018. PMID: 30541778 Free PMC article.
-
The Odilorhabdin Antibiotic Biosynthetic Cluster and Acetyltransferase Self-Resistance Locus Are Niche and Species Specific.mBio. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):e0282621. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02826-21. Epub 2022 Jan 11. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35012352 Free PMC article.
-
The promise of endogenous and exogenous riboflavin in anti-infection.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):2314-2326. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1963909. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34490839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wars and sweets: microbes, medicines and other moderns in and beyond the(ir) antibiotic era.Med Humanit. 2022 Aug 10;48(3):359-70. doi: 10.1136/medhum-2021-012366. Online ahead of print. Med Humanit. 2022. PMID: 35948395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernard S, Papineau D. Graphitic carbons and biosignatures. Elements. 2014;10(6):435–40. doi: 10.2113/gselements.10.6.435. - DOI
-
- Landan G, Cohen G, Aharonowitz Y, Shuali Y, Graur D, Shiffman D. Evolution of isopenicillin N synthase genes may have involved horizontal gene transfer. Mol Biol Evol. 1990;7(5):399–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

