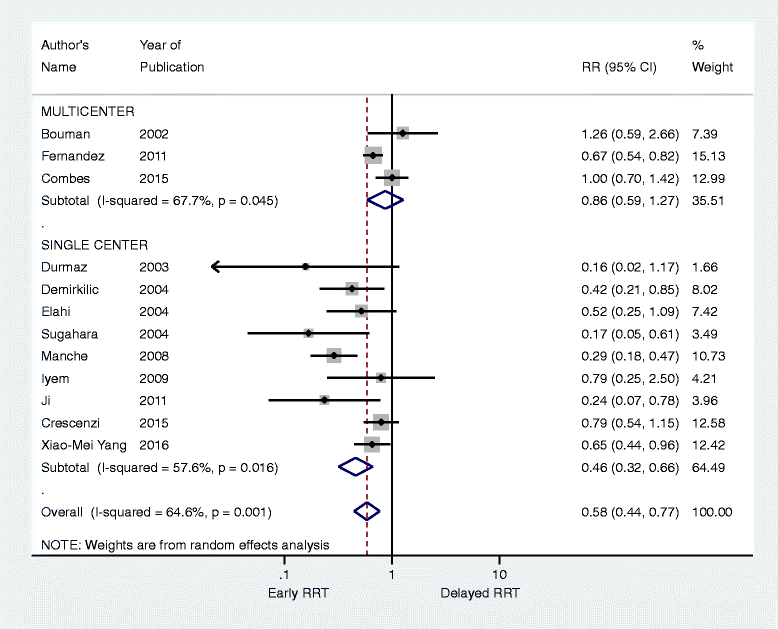
Accounting for single center effects in systematic reviews cannot be overlooked
- PMID: 28915905
- PMCID: PMC5602911
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1804-0
Accounting for single center effects in systematic reviews cannot be overlooked
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Comment on
-
Early versus late initiation of renal replacement therapy impacts mortality in patients with acute kidney injury post cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2017 Jun 17;21(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1707-0. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28623953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources