Early sepsis detection in critical care patients using multiscale blood pressure and heart rate dynamics
- PMID: 28916175
- PMCID: PMC5696025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2017.08.013
Early sepsis detection in critical care patients using multiscale blood pressure and heart rate dynamics
Abstract
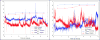
Sepsis remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among intensive care unit (ICU) patients. For each hour treatment initiation is delayed after diagnosis, sepsis-related mortality increases by approximately 8%. Therefore, maximizing effective care requires early recognition and initiation of treatment protocols. Antecedent signs and symptoms of sepsis can be subtle and unrecognizable (e.g., loss of autonomic regulation of vital signs), causing treatment delays and harm to the patient. In this work we investigated the utility of high-resolution blood pressure (BP) and heart rate (HR) times series dynamics for the early prediction of sepsis in patients from an urban, academic hospital, meeting the third international consensus definition of sepsis (sepsis-III) during their ICU admission. Using a multivariate modeling approach we found that HR and BP dynamics at multiple time-scales are independent predictors of sepsis, even after adjusting for commonly measured clinical values and patient demographics and comorbidities. Earlier recognition and diagnosis of sepsis has the potential to decrease sepsis-related morbidity and mortality through earlier initiation of treatment protocols.
Keywords: Critical care; Dynamics; ECG; Infection; Machine learning; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally ME, Rochwerg B. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Medicine. 2017 Mar 1;43(3):304–77. - PubMed
-
- Frost R, Newsham H, Parmar S, Gonzalez-Ruiz A. Impact of delayed antimicrobial therapy in septic ITU patients. Critical Care. 2010 Apr 1;14(S2):P20.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

