Breast cancer vaccines delivered by dendritic cell-targeted lentivectors induce potent antitumor immune responses and protect mice from mammary tumor growth
- PMID: 28916248
- PMCID: PMC5624555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.09.017
Breast cancer vaccines delivered by dendritic cell-targeted lentivectors induce potent antitumor immune responses and protect mice from mammary tumor growth
Abstract
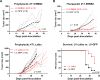
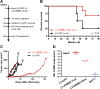
Breast cancer immunotherapy is a potent treatment option, with antibody therapies such as trastuzumab increasing 2-year survival rates by 50%. However, active immunotherapy through vaccination has generally been clinically ineffective. One potential means of improving vaccine therapy is by delivering breast cancer antigens to dendritic cells (DCs) for enhanced antigen presentation. To accomplish this in vivo, we pseudotyped lentiviral vector (LV) vaccines with a modified Sindbis Virus glycoprotein so that they could deliver genes encoding the breast cancer antigen alpha-lactalbumin (Lalba) or erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (ERBB2 or HER2) directly to resident DCs. We hypothesized that utilizing these DC-targeting lentiviral vectors asa breast cancer vaccine could lead to an improved immune response against self-antigens found in breast cancer tumors. Indeed, single injections of the vaccine vectors were able to amplify antigen-specific CD8T cells 4-6-fold over naïve mice, similar to the best published vaccine regimens. Immunization of these mice completely inhibited tumor growth in a foreign antigen environment (LV-ERBB2 in wildtype mice), and it reduced the rate of tumor growth in a self-antigen environment (LV-Lalba in wildtype or LV-ERBB2 in MMTV-huHER2 transgenic). These results show that a single injection with targeted lentiviral vectors can be an effective immunotherapy for breast cancer. Furthermore, they could be combined with other immunotherapeutic regimens to improve outcomes for patients with breast cancer.
Keywords: Alpha-lactalbumin; Breast cancer immunotherapy; Cancer vaccine; ERBB2/Her2; Lentiviral vector.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

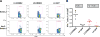
Similar articles
-
Dendritic cell-directed lentivector vaccine induces antigen-specific immune responses against murine melanoma.Cancer Gene Ther. 2011 May;18(5):370-80. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2011.13. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011. PMID: 21372855
-
DNA vaccines targeting the encoded antigens to dendritic cells induce potent antitumor immunity in mice.BMC Immunol. 2013 Aug 14;14:39. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-14-39. BMC Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23941509 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor protection following vaccination with low doses of lentivirally transduced DCs expressing the self-antigen erbB2.Mol Ther. 2008 Mar;16(3):607-17. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300390. Epub 2008 Jan 8. Mol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18180774
-
DNA vaccine for cancer immunotherapy.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3153-64. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.980686. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lentiviral vectors for anti-tumor immunotherapy.Curr Gene Ther. 2008 Dec;8(6):438-48. doi: 10.2174/156652308786848058. Curr Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 19075627 Review.
Cited by
-
Plant Viruses and Bacteriophage-Based Reagents for Diagnosis and Therapy.Annu Rev Virol. 2020 Sep 29;7(1):559-587. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-010720-052252. Annu Rev Virol. 2020. PMID: 32991265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Vector-Based Cancer Vaccines.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2926:101-127. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4542-0_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40266521
-
Pseudotyped lentiviral vectors: Ready for translation into targeted cancer gene therapy?Genes Dis. 2022 Apr 2;10(5):1937-1955. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.03.007. eCollection 2023 Sep. Genes Dis. 2022. PMID: 37492721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic and Local Strategies for Primary Prevention of Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 5;16(2):248. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020248. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic cells modified by tumor associated antigen SMP30 have enhanced antitumor effect against mouse hepatocarcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Aug 15;14(8):5785-5799. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36105050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;344(11):783–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

