Measuring progress and projecting attainment on the basis of past trends of the health-related Sustainable Development Goals in 188 countries: an analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016
- PMID: 28916366
- PMCID: PMC5603800
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32336-X
Measuring progress and projecting attainment on the basis of past trends of the health-related Sustainable Development Goals in 188 countries: an analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016
Erratum in
-
Department of Error.Lancet. 2017 Sep 30;390(10102):e23. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32441-8. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28935159 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Department of Error.Lancet. 2017 Oct 28;390(10106):e38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32650-8. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 29032990 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are grounded in the global ambition of "leaving no one behind". Understanding today's gains and gaps for the health-related SDGs is essential for decision makers as they aim to improve the health of populations. As part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2016 (GBD 2016), we measured 37 of the 50 health-related SDG indicators over the period 1990-2016 for 188 countries, and then on the basis of these past trends, we projected indicators to 2030.
Methods: We used standardised GBD 2016 methods to measure 37 health-related indicators from 1990 to 2016, an increase of four indicators since GBD 2015. We substantially revised the universal health coverage (UHC) measure, which focuses on coverage of essential health services, to also represent personal health-care access and quality for several non-communicable diseases. We transformed each indicator on a scale of 0-100, with 0 as the 2·5th percentile estimated between 1990 and 2030, and 100 as the 97·5th percentile during that time. An index representing all 37 health-related SDG indicators was constructed by taking the geometric mean of scaled indicators by target. On the basis of past trends, we produced projections of indicator values, using a weighted average of the indicator and country-specific annualised rates of change from 1990 to 2016 with weights for each annual rate of change based on out-of-sample validity. 24 of the currently measured health-related SDG indicators have defined SDG targets, against which we assessed attainment.
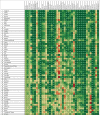
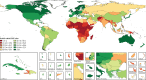
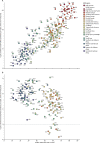
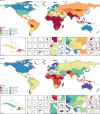
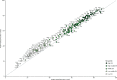
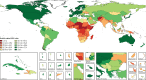
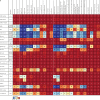
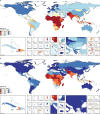
Findings: Globally, the median health-related SDG index was 56·7 (IQR 31·9-66·8) in 2016 and country-level performance markedly varied, with Singapore (86·8, 95% uncertainty interval 84·6-88·9), Iceland (86·0, 84·1-87·6), and Sweden (85·6, 81·8-87·8) having the highest levels in 2016 and Afghanistan (10·9, 9·6-11·9), the Central African Republic (11·0, 8·8-13·8), and Somalia (11·3, 9·5-13·1) recording the lowest. Between 2000 and 2016, notable improvements in the UHC index were achieved by several countries, including Cambodia, Rwanda, Equatorial Guinea, Laos, Turkey, and China; however, a number of countries, such as Lesotho and the Central African Republic, but also high-income countries, such as the USA, showed minimal gains. Based on projections of past trends, the median number of SDG targets attained in 2030 was five (IQR 2-8) of the 24 defined targets currently measured. Globally, projected target attainment considerably varied by SDG indicator, ranging from more than 60% of countries projected to reach targets for under-5 mortality, neonatal mortality, maternal mortality ratio, and malaria, to less than 5% of countries projected to achieve targets linked to 11 indicator targets, including those for childhood overweight, tuberculosis, and road injury mortality. For several of the health-related SDGs, meeting defined targets hinges upon substantially faster progress than what most countries have achieved in the past.
Interpretation: GBD 2016 provides an updated and expanded evidence base on where the world currently stands in terms of the health-related SDGs. Our improved measure of UHC offers a basis to monitor the expansion of health services necessary to meet the SDGs. Based on past rates of progress, many places are facing challenges in meeting defined health-related SDG targets, particularly among countries that are the worst off. In view of the early stages of SDG implementation, however, opportunity remains to take actions to accelerate progress, as shown by the catalytic effects of adopting the Millennium Development Goals after 2000. With the SDGs' broader, bolder development agenda, multisectoral commitments and investments are vital to make the health-related SDGs within reach of all populations.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article published under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Political determinants of Sustainable Development Goals.Lancet. 2017 Dec 9;390(10112):2545-2546. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33082-9. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 29231829 No abstract available.
References
-
- UN . Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2015.
-
- High-Level Political Forum (HLPF) 2017 HLPF Thematic Review of SDG3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. 2017. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/14367SDG3format-... (accessed June 15, 2017).
-
- UN . The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2017. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2017.
-
- McIntyre D, McKee M, Balabanova D, Atim C, Reddy KS, Patcharanarumol W. Open letter on the SDGs: a robust measure for universal health coverage is essential. Lancet. 2016;388:2871–2872. - PubMed
-
- United Nations Statistical Commission . Report of the inter-agency and expert group on Sustainable Development Goal Indicators. UN Statistical Commission; New York, NY, USA: 2017.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH110163/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG047845/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- D43 TW009775/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U147585819/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 201900/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- SPHSU13/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HD087993/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- SCAF/15/02/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585824/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI112339/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 201900/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12017/13/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U147585827/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AI096299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD084233/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M015084/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SPHSU15/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- U54 HG007479/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K013351/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12011/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI124389/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12017/15/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400491/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CDF-2011-04-048/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

