Interactions between medial prefrontal cortex and dorsomedial striatum are necessary for odor span capacity in rats: role of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors
- PMID: 28916627
- PMCID: PMC5602347
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.045419.117
Interactions between medial prefrontal cortex and dorsomedial striatum are necessary for odor span capacity in rats: role of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors
Abstract
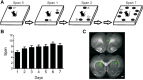
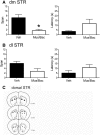
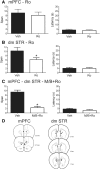
Working memory is involved in the maintenance and manipulation of information essential for complex cognition. While the neural substrates underlying working memory capacity have been studied in humans, considerably less is known about the circuitry mediating working memory capacity in rodents. Therefore, the present experiments tested the involvement of medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and dorsal striatum (STR) in the odor span task (OST), a task proposed to assay working memory capacity in rodents. Initially, Long Evans rats were trained to dig in scented sand for food following a serial delayed nonmatching-to-sample rule. Temporary inactivation of dorsomedial (dm) STR significantly reduced span in well trained rats. Inactivation of mPFC or contralateral disconnection of the mPFC and dmSTR also reduced span. Infusing the GluN2B-containing NMDA receptor antagonist Ro 25-6981 into mPFC did not affect span; however, span was significantly reduced following bilateral Ro 25-6981 infusions into dmSTR or contralateral disconnection of mPFC (inactivation) and dmSTR (Ro 25-6981). These results suggest that span capacity in rats depends on GluN2B-containing NMDA receptor-dependent interactions between the mPFC and the dmSTR. Therefore, interventions targeting this circuit may improve the working memory capacity impairments in patients with schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease.
© 2017 Davies et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors and AMPA receptors in medial prefrontal cortex are necessary for odor span in rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2013 Dec 2;7:183. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00183. eCollection 2013. Front Behav Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24348356 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the medial prefrontal cortex, mediodorsal thalamus, and their combined circuit for performance of the odor span task in rats: analysis of memory capacity and foraging behavior.Learn Mem. 2020 Jan 16;27(2):67-77. doi: 10.1101/lm.050195.119. Print 2020 Feb. Learn Mem. 2020. PMID: 31949038 Free PMC article.
-
Medial prefrontal cortex and dorsomedial striatum are necessary for the trial-unique, delayed nonmatching-to-location (TUNL) task in rats: role of NMDA receptors.Learn Mem. 2017 May 15;24(6):262-266. doi: 10.1101/lm.044750.116. Print 2017 Jun. Learn Mem. 2017. PMID: 28507036 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory modulation of the medial prefrontal cortex circuitry: Implications for social cognition.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep;129:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.03.022. Epub 2021 May 9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 33975755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuroanatomy and neurochemistry of schizophrenia.Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1998 Mar;21(1):57-75. doi: 10.1016/s0193-953x(05)70361-0. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1998. PMID: 9551491 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcranial direct current stimulation relieves visceral hypersensitivity via normalizing GluN2B expression and neural activity in anterior cingulate cortex.J Neurophysiol. 2021 May 1;125(5):1787-1797. doi: 10.1152/jn.00025.2021. Epub 2021 Mar 24. J Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 33760644 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of NMDA antagonist dizocilpine (MK-801) are modulated by the number of distractor stimuli in the rodent odor span task of working memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019 May;161:51-56. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.03.004. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019. PMID: 30862525 Free PMC article.
-
The rodent medial prefrontal cortex and associated circuits in orchestrating adaptive behavior under variable demands.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Apr;135:104569. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104569. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 35131398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleus accumbens core dopamine D2 receptors are required for performance of the odor span task in male rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 May;241(5):963-974. doi: 10.1007/s00213-023-06522-4. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38183429
-
Olfactory Information Storage Engages Subcortical and Cortical Brain Regions That Support Valence Determination.Cereb Cortex. 2022 Feb 8;32(4):689-708. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhab226. Cereb Cortex. 2022. PMID: 34379749 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
