Differential Expression of miRNAs in the Respiratory Tree of the Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Under Hypoxia Stress
- PMID: 28916650
- PMCID: PMC5677170
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.117.1129
Differential Expression of miRNAs in the Respiratory Tree of the Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Under Hypoxia Stress
Abstract
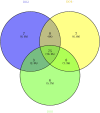
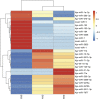
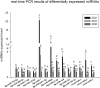
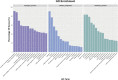
The sea cucumber, an important economic species, has encountered high mortality since 2013 in northern China because of seasonal environmental stress such as hypoxia, high temperature, and low salinity. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are important in regulating gene expression in marine organisms in response to environmental change. In this study, high-throughput sequencing was used to investigate alterations in miRNA expression in the sea cucumber under different levels of dissolved oxygen (DO). Nine small RNA libraries were constructed from the sea cucumber respiratory trees. A total of 26 differentially expressed miRNAs, including 12 upregulated and 14 downregulated miRNAs, were observed in severe hypoxia (DO 2 mg/L) compared with mild hypoxia (DO 4 mg/L) and normoxic conditions (DO 8 mg/L). Twelve differentially expressed miRNAs were clustered in severe hypoxia. In addition, real-time PCR revealed that 14 randomly selected differentially expressed miRNAs showed significantly increased expressions in severe hypoxia and the expressions of nine miRNAs, including key miRNAs such as Aja-miR-1, Aja-miR-2008, and Aja-miR-184, were consistent with the sequencing results. Moreover, gene ontology and pathway analyses of putative target genes suggest that these miRNAs are important in redox, transport, transcription, and hydrolysis under hypoxia stress. Notably, novel-miR-1, novel-miR-2, and novel-miR-3 were specifically clustered and upregulated in severe hypoxia, which may provide new insights into novel "hypoxamiR" identification. These results will provide a basis for future studies of miRNA regulation and molecular adaptive mechanisms in sea cucumbers under hypoxia stress.
Keywords: Illumina deep sequencing; hypoxia stress; miRNA; respiratory tree; sea cucumber.
Copyright © 2017 Huo et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding regulation of microRNAs on intestine regeneration in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus using high-throughput sequencing.Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2017 Jun;22:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28160609
-
Large-scale identification and comparative analysis of miRNA expression profile in the respiratory tree of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during aestivation.Mar Genomics. 2014 Feb;13:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Mar Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24444870
-
Sea cucumbers in a high temperature and low dissolved oxygen world: Roles of miRNAs in the regulation of environmental stresses.Environ Pollut. 2021 Jan 1;268(Pt A):115509. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115509. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Environ Pollut. 2021. PMID: 33038634
-
MicroRNAs involved in innate immunity regulation in the sea cucumber: A review.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Dec;95:297-304. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.10.049. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31669896 Review.
-
MiR-210--micromanager of the hypoxia pathway.Trends Mol Med. 2010 May;16(5):230-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.03.004. Epub 2010 Apr 29. Trends Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20434954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic profiling to environmental stressors in model and non-model organisms: Ecotoxicology perspective.Environ Health Toxicol. 2018 Sep;33(3):e2018015-0. doi: 10.5620/eht.e2018015. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Environ Health Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30286591 Free PMC article.
-
Salinity stress-induced differentially expressed miRNAs and target genes in sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2019 Jul;24(4):719-733. doi: 10.1007/s12192-019-00996-y. Epub 2019 May 27. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2019. PMID: 31134533 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation mechanism of lncRNAs and mRNAs in sea cucumbers under global climate changes: Defense against thermal and hypoxic stresses.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Mar 20;709:136045. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136045. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 31905562 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of hypoxia stress on the physiological responses of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus: respiration, digestion, immunity and oxidative damage.PeerJ. 2018 Apr 27;6:e4651. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4651. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 29719735 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and functional characterization of a novel TRPA1 gene from sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus and interaction with miR-2013 in response to salt stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Nov;28(6):1027-1039. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01398-x. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 38108989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson G. R., Stoler D. L., Scarcello L. A., 1989. Normal fibroblasts responding to anoxia exhibit features of the malignant phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 14885–14892. - PubMed
-
- Bartel D. P., 2004. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Biggar K. K., Kornfeld S. F., Maistrovski Y., Storey K. B., 2012. MicroRNA regulation in extreme environments: differential expression of microRNAs in the intertidal snail Littorina littorea during extended periods of freezing and anoxia. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 10: 302–309. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
